Precautionary measures. Traffic rules and travel within the intersection
Approaching such intersections is recommended at a lower speed than constant - depending on the landscape, road and weather factors.
It is important not to forget the fact that any road intersection, even the most harmless one, is an area of increased risk of an accident. A clean asphalt surface can become contaminated as a result of adverse weather conditions and many other factors (oil film, for example)
Vigilance and careful attention to signs and road markings will protect you from force majeure at any (not only T-shaped) intersections - be it a suddenly appearing car, a forest animal or livestock.
How to get through an uncontrolled T-junction
Rules for driving through unregulated intersections
Like any other intersection, the type under consideration is divided into two types: unequal and equivalent T-shaped intersection.
An equivalent intersection is not subject to any signage. All vehicles moving along it must necessarily give way to those vehicles moving on the right. In addition, when turning left at an equivalent intersection, the driver is obliged to give way to all cars moving straight in the opposite direction.
A T-shaped intersection of lanes is considered unequal if there is a sign in front of it. An intersection with such a sign must have a main and secondary road. Any driver knows that cars driving on a secondary road are required to give priority to those driving in the main direction. As with an equivalent intersection, drivers who choose to turn left are required to give priority to all vehicles traveling straight ahead in the oncoming lane.
There is another rule for driving through an equivalent intersection. If a driver turns off the main road, he has priority over other cars that are in the secondary lane.
Driving through a T-junction of equivalent roads
If traffic lights (adjustable) or priority signs (unequal) are installed at the intersection, then the order of passage does not raise questions among drivers.
However, if there is a T- junction on the road without signs, i.e. equivalent , then misunderstandings often arise.
Consider the following figure:
Drivers must be guided by paragraphs 13.11 and 13.12 of the traffic rules:
13.11. At the intersection of equivalent roads, with the exception of the case provided for in paragraph 13.11 1 of the Rules, the driver of a trackless vehicle is obliged to give way to vehicles approaching from the right.
13.12. When turning left or making a U-turn, the driver of a trackless vehicle is obliged to give way to vehicles moving on an equivalent road from the opposite direction straight or to the right.
Rules for driving from a one-way track
Rules for turning around tram tracks outside an intersection
In the event of a change in the trajectory of the priority road, at an unregulated T-intersection there must be a plate 8.13, installed together with the road signs under paragraphs 2.1 and 2.4. You must immediately determine what the road is along which you approached the intersection and whether you have the right of way. First, vehicles that approached it along the priority route pass through the unregulated intersection.
T-junctions, mostly unregulated, outside populated areas are a common occurrence. Drivers (who have priority) will be aware of their approach to it by the signs under paragraphs 2.3.2 to 2.3.7, which means an adjacent secondary road,” while on the minor roads before the intersection of roads there are signs under paragraph 2.4, which means “ Give way”, under paragraph 2.5 - which means prohibition of movement without first stopping. Taking into account the high speeds of vehicles outside populated areas, travel from a secondary route to such an intersection requires extreme concentration of attention, because vehicles that have priority in traffic move at a higher speed than one can imagine.
Markings at a T-junction
It is important to take into account the markup, as many nuances depend on it.
Particular attention should be paid to it when turning, as you may simply not fit into it if the road is narrow or the car is large. In this case, the markings will help determine the boundaries of the turn.
There is often a stop sign before a road intersection, indicating that the vehicle must be stopped before entering. To do this, there is a line on the road in front of which the car must stop.
Markings play an important role in determining the possibility of stopping at an intersection. Usually this cannot be done, but there are exceptions. If part of the road in the upper section is separated by a solid marking line, then stopping on it is permitted subject to additional conditions: there must be more than three meters from the marking line to the car, and there should be no intersections with other roads at a distance of five meters to it.
Issues relating to motorists' rights are often more important than they appear at first glance. A driver may lose his license or suffer other severe penalties due to ignorance or misinterpretation of laws and regulations. Do not be lazy to dive deeply into the essence of the issue being studied, do not hesitate to ask advice from professionals.
Locality
Rules for driving through intersections. Driving through controlled intersections
In the traffic rules there are no concepts of “city”, “village”, “metropolis” or “country”. There are sections of roads designated as “populated area” or “outside the populated area.” And these areas are indicated by corresponding signs.
Consequently, in Russian traffic practice there are three main sections of the road: a populated area, outside a populated area and a highway.
. Such areas differ in the requirements that are imposed on drivers moving along them. And the main requirement is maximum speed.
But, returning to the concept of a settlement, one should ask the question: “Why are there three signs indicating this area?” For one concept – three signs at once? Let's figure it out.
“Settled area” signs - black on white - mean that on this section of the road there are rules governing traffic in a populated area. Let’s call such a site a “real populated area.” That is, the general maximum speed limit here is no more than 60 km/h.
The second type of sign “Settled area” - white on blue - indicates a section of the road where traffic rules outside a populated area apply. In other words, the maximum speed here is classically limited - no more than 90 km/h (for vehicles of category B). As it should be outside the populated area!
A reasonable question arises: “Why is the last sign needed?” Or this: “Why call a site a populated area if it is not one?”
And it exists to inform the driver that he is passing by this very populated area, but has not yet entered it (and may not enter it until he encounters a “Settled Area” sign on his way - black on white!). But even here elements of the infrastructure of a settlement can be concentrated: bus stops, an abundance of intersections, pedestrian crossings, tram tracks, etc. But this is not a populated area!
Of course, such a mixture of concepts and signs is an absolute confusion. But these are our traffic rules that we must follow and comply with. Unfortunately, there are no others!
T-junction rules
- Adjustable. Driving through an intersection where the order of passage is regulated, as a rule, does not cause any difficulties. If the roadway consists of several traffic lanes and is equipped with a marking line (according to clause 1.18 of the traffic rules), and is also equipped with signs regulating the direction of travel along the lanes (clause 5.15.2 of the traffic rules), then you must follow them. In any case, in advance, before starting the maneuver, the driver must change lanes to the appropriate lane. Start driving only when the traffic light (or traffic controller) gives permission. If the traffic light has an additional section with an arrow, then when the indicator is activated in green, together with the main red traffic light signal, before moving, other vehicles should be given priority in moving (that is, you can move if this does not interfere with other road users ).
- Unregulated. Depending on the presence or absence of priority signs (road signs 2.1, 2.3.2-2.3.7, 2.4), an intersection can be formed by the intersection of equivalent and unequal roads. If the intersection is made up of unequal roads, when performing maneuvers you should be guided by signs that give priority when moving. A vehicle moving on a secondary road must give way to all vehicles moving on the main road. When changing the direction of the main road, both vehicle drivers on it must allow all traffic participants moving on the right side of it to pass, that is, such an intersection is passed by analogy with an intersection formed by the intersection of equivalent roads. If signs giving priority are not identified, then you should move along such an intersection according to the rules for equivalent roads.
- If the intersection is equal, then the driver is obliged to give priority to those vehicles moving to the right of him. When making a left turn or a U-turn, you must also give way to those vehicles located in the oncoming lane of the driver performing the maneuver.
If the order of passage through an intersection is regulated (by a traffic light or a traffic controller), this kind of intersection is called controlled. If there is no adjustment, it is called unregulated. Also, depending on the signs that give priority when driving, intersections can be equivalent or unequal. Let's consider the order of passage of different types of intersections.
More information about driving through T-junctions
T-junctions are simpler than regular ones, they have a clearer and more convenient form, which reduces the risk of dangerous situations. In addition, only three parties are involved in them, which means there will be fewer participants in the movement.
In principle, the traffic rules do not distinguish them into a separate category, so there are no special rules for them.
T-intersections intersect according to the same rules as other intersections, although their unusual shape gives them some peculiarities.
Adjacent territory
In addition to the roads themselves, the road transport network of the Russian Federation also includes a number of sections along which traffic occurs, but which, according to traffic regulations, are not roads. We are talking about the surrounding area.
By definition, the adjacent area is adjacent (or adjacent) to the road. And therefore she herself is not considered such. This, of course, is a controversial statement, but it follows from the very letter of the Rules.
The adjacent territory includes areas where through traffic is prohibited:
1) gas stations;
2) courtyard areas;
3) parking places for vehicles;
4) territories of enterprises, institutions, etc.
Unfortunately, it is very problematic to accurately determine the exit from the adjacent territory. And this question is fundamental. The fact is that such exits are not considered intersections. The term “intersection” can be applied to them, but not “intersection of roadways” (or intersection).
And the principle of the question is as follows. For example, the nine most odious (including signs prohibiting overtaking, stopping, parking, limiting the maximum speed, etc.) are canceled by the intersection closest to the direction of travel.
Therefore, a driver who recognizes himself and mistakes the exit from the adjacent territory as an intersection risks violating the Rules and being punished for violating the requirements of these signs. In the future, a fine or even deprivation of your driver's license!
That is why you need to sacredly remember the rule: leaving the adjacent territory (or entering it) is not an intersection!
Rules for driving at controlled intersections
The rules for driving through intersections with traffic lights are regulated by the traffic lights (which are the main ones) and the signals of additional sections.
Vehicles moving on the main green traffic light must determine priority among themselves in accordance with the “interference on the right” rule. Let's say you're turning left at a crossroads, and an oncoming car is moving straight ahead. When the green light turns on, you must enter the intersection, starting the maneuver, and let the oncoming car pass, and only then complete the turn.
If the red or yellow signals and the additional section of the traffic light are on at the same time, first let through all vehicles for which the main green signal is on, and only then move in the direction indicated by the signal of the additional section.
Video lesson: driving through intersections according to the rules.
Crossroads
The intersection seems to be an incredibly complex and important section of the road. No matter how the driver tries to avoid meeting him, it will not work. This is where the paths of vehicles and pedestrians intersect. This is where they “work” as much as possible: someone takes advantage, and someone must give way.
Let's try to understand the intricacies of this definition and the concept of “crossroads” in general.
1. An intersection is a section formed by the intersection (junction, branching) of roads in the same plane.
From this we conclude that driving under a bridge, overpass or overpass will not be considered an intersection.
The intersection of roads must be real - at the same level (or - it would be more correct to say - in the same plane).
2. From the definition proposed in the traffic rules, it is very difficult to imagine the structure of the intersection. But if you look at it in detail, the intersection is not only the intersection of roadways; it is wider and begins at the corners of curbs or shoulders.
3. The question of the types of intersections is fundamental. After all, there are a huge number of them:
a) classic four-digit (or “cruciform”) intersection;
b) an intersection without one side passage (T-shaped intersection);
c) three-digit Y-intersection.
An intersection can also have a rather complex architecture, where you can encounter not just one intersection of roadways, but 2 or more.
At the intersection shown in the figure above, there are two roadways crossing each other. And this question will be fundamental when studying road signs. There are simply signs (for example, prescriptive 4.1-4.6) that act precisely at the intersection in front of which the sign is installed.
And there are signs that can apply to the entire intersection (for example, “Main Road”).
Therefore, the number of roadway crossings is an important indicator of an intersection.
Another complex intersection with a roundabout has a special status.
The rules for its passage are a separate matter.
The driver’s task is to clearly know the rules for driving through any intersection that he encounters on his way. And we will definitely be faced with this problem in the future.
And one last thing. According to traffic regulations, exits from adjacent territories (and, consequently, entrances to them) are not intersections. Let’s look at what this “adjacent territory” is next.
Stop at a T-junction
Traffic rules prohibit stopping at intersections of roadways:
However, paragraph 12.4 provides an exception, which specifically includes T-shaped intersections:
12.4. Stopping is prohibited: .
- at the intersection of roadways and closer than 5 m from the edge of the roadway being crossed, with the exception of the side opposite the side passage of three-way intersections (crossroads) that have a continuous marking line or dividing strip;
That is, the possibility of parking at a T-shaped intersection depends on what kind of markings are applied at the intersection.
If the marking is solid or double solid (left picture), then you can stop.
If the markings are intermittent, continuous with intermittent ones, or absent altogether, then you cannot park at the intersection.
Note. At the intersection, a rule must also be observed that requires stopping no closer than 3 meters from the markings .
Well, if you want to study the rules for driving through intersections in more detail, I recommend studying all the articles in the series:
There are different types of intersections and each of them has its own rules. In addition to ordinary ones, there are often T-intersections, when one part of the road runs perpendicular to another. To move safely around the city, every driver must know the rules for driving through T-intersections.
What is a T-shaped intersection of stripes
First of all, it is worth noting that the T-shaped intersection of stripes cannot be separated into any separate category. In addition, the concept of “T-shaped intersection” is absent in the traffic rules
It is important to understand that, in principle, driving through this type of intersection is no different from any other type, so in practice you can safely apply the same traffic rules
In order to understand for sure how to drive through T-shaped intersections, it is necessary to analyze all possible situations to the maximum. In addition, it is worth considering the rules for crossing lanes for cyclists, because traffic rules for motorists and cyclists are sometimes very different.
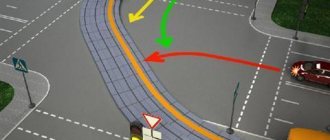
Rules for turning around at a T-junction
Traffic regulations do not impose restrictions on turning at three-way intersections. However, the following should be considered:
- Before turning, the car must take the extreme left position on the roadway in this direction (clause 8.5).
- At the intersection, reversing is prohibited (Section 8.12 of the Traffic Regulations).
Look at the picture above
Notice the orange car. His driver took the extreme left position, as required by the rules
However, it is obvious that he does not have enough width of the roadway to complete the turn.
Those. despite the fact that the rules allow you to turn around
at T-shaped intersections, it should be taken into account that this will not be possible at every intersection.
In addition, do not confuse a U-turn at an intersection with a U-turn using the surrounding area, which is offered in (tickets 9-19 and 12-19):
The indicated turning patterns can only be used in adjacent territories, because Reversing is prohibited at intersections.
Overtaking is only possible if the car is moving straight through the intersection. In this case, 2 conditions must be met:
- The intersection is unregulated (no traffic controller or traffic lights).
- The driver is on the main road, which goes straight.
The left picture shows an equivalent intersection and overtaking is prohibited at it.
The picture on the right shows a unequal intersection that is joined by a secondary road. At such an intersection, overtaking is not prohibited, but the driver must follow the overtaking rules.
Traffic rules prohibit stopping at intersections of roadways:
However, paragraph 12.4 provides an exception, which specifically includes T-shaped intersections:
That is, the possibility of parking at a T-shaped intersection depends on what kind of markings are applied at the intersection.
If the marking is solid or double solid (left picture), then you can stop.
If the markings are intermittent, continuous with intermittent ones, or absent altogether, then you cannot park at the intersection.
Note. At the intersection there must also be a rule that requires stopping no closer than 3 meters from the markings.
.
Well, if you want to study the rules for driving through intersections in more detail, I recommend studying all the articles in the series:
Gennady-44
Why is it forbidden to mark 1.11 on the solid side at a T-shaped intersection?
Gennady
, paragraph 12.4 of the traffic rules states that the markings must be continuous. Marking 1.11 is partially intermittent, so you cannot stop at the intersection.
Good luck on the roads!
The above is relevant mainly for roads outside populated areas. In the NP, according to GOST, the “Main Road” sign must be repeated before each intersection, so its disappearance is a good reason for drivers to slow down and look around for changed priorities.
Is it possible to turn around if there is no left turn (orange car)?
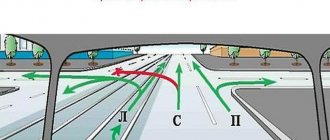
Please tell me, when turning left, at the base of a figurative intersection, at what point should I give way to an oncoming car? Before the intersection or take the center, let it pass and only then go?
If the intersection is equivalent, then you can go to the center. You have priority over the one leaving the base, so if he also goes to the left, then he must give way to you. If the intersection is unequal and you are on a secondary road, then you need to stop before crossing.
An exception is if the base is so narrow that oncoming traffic is difficult, and a car has also approached from the base and is about to turn left. In this case, even if the base is secondary (a narrow dirt road, for example), it is better to stop before the intersection, “let go” of the person leaving, and only then turn. There is no such requirement in the traffic rules, well, except for requirement 8.1 in the part “not to create interference.” But it will be easier for you than to “push” the driver back onto the secondary road and then have to pass each other on a narrow road.
A T-shaped intersection, I approached the center and was about to turn left, but then I saw a car opposite, I stopped to let it pass, and the instructor counted it as a stop at the intersection. So I had to wait on the median?
Giving way to oncoming traffic while complying with traffic rules 13.12 is not a violation of either 12.4 (intentional stopping) or 13.2 (entering an intersection with a traffic jam). What violation did the instructor give you: a violation of stopping rules, a violation of turning rules, or something else?
You can stop before the intersection
, if you think that it will be more convenient for everyone to pass the intersection this way (first on the left, then with the oncoming person, then you), but you do not have such an obligation.
Overtaking at a T-junction
Overtaking is only possible if the car is moving straight through the intersection. In this case, 2 conditions must be met:
- The intersection is unregulated (no traffic controller or traffic lights).
- The driver is on the main road, which goes straight.
The left picture shows an equivalent intersection and overtaking is prohibited at it.
The picture on the right shows a unequal intersection that is joined by a secondary road. At such an intersection, overtaking is not prohibited, but the driver must follow the overtaking rules.
Rules for driving at a controlled T-junction
If the intersection is equipped with a traffic light, then, as a rule, drivers do not have any difficulties
The only thing that always needs to be taken into account is that absolutely all installed signs and markings on the road should be taken into account and observed. You must move strictly along the lanes and do not violate the order of travel.
Signalized intersections are very simple, which is why the fewest accidents occur at them. The T-shaped intersection of stripes is no exception.
If a traffic light with an additional section is installed at an intersection, then in this case, traffic participants who move along this lane must give priority to those cars that move according to the main traffic light signal. Simply put, cars driving on a green traffic light with an additional section can make maneuvers without restrictions, but only if they do not interfere with other vehicles.
Like any other intersection, the type under consideration is divided into two types: unequal and equivalent T-shaped intersection.
An equivalent intersection is not subject to any signage. All vehicles moving along it must necessarily give way to those vehicles moving on the right. In addition, when turning left at an equivalent intersection, the driver is obliged to give way to all cars moving straight in the opposite direction.
A T-shaped intersection of lanes is considered unequal if there is a sign in front of it. An intersection with such a sign must have a main and secondary road. Any driver knows that cars driving on a secondary road are required to give priority to those driving in the main direction. As with an equivalent intersection, drivers who choose to turn left are required to give priority to all vehicles traveling straight ahead in the oncoming lane.
There is another rule for driving through an equivalent intersection. If a driver turns off the main road, he has priority over other cars that are in the secondary lane.
Sometimes there are situations when a vehicle approaches an intersection where one road is one-way and the other is not. What to do in this situation?
So, a driver must drive through a T-junction on a one-way road in the same way as a regular intersection. Traffic rules state that it is necessary to change into the outer lane for a turn in advance, so as not to interfere with other vehicles. Also, do not forget that this type of intersection, as a rule, is not equipped with a traffic light, which means that the driver must give way to vehicles moving on the right.
It is important to know that driving on a one-way road towards oncoming traffic is strictly prohibited. This is punishable by a heavy fine or deprivation of the right to drive a vehicle for up to six months.
Now it is necessary to analyze the situation when a driver drives from a one-way road to a two-way road. This may be a T-junction or a regular intersection.
As usual, the driver must first change lanes into the lane in which he is going to turn.
Most likely, there will also be no traffic lights or traffic signs installed at the road intersection, so it is important to watch for vehicles on the right, which are called “interference on the right” among drivers. Traffic regulations require maximum care and accuracy from the driver
After the driver is convinced that he can drive safely and nothing is bothering him, he has the right to safely make a maneuver.
This type of intersection does not differ from the usual one, even when performing a maneuver such as a U-turn. The rules for driving through a T-shaped intersection, or rather making a U-turn, provide for only one limitation - you can perform this maneuver while driving exclusively in a passenger car. Larger models, such as trucks or SUVs, will no longer be able to make a U-turn in confined spaces, and driving in reverse at road intersections is prohibited.
When the driver begins to turn around at a T-shaped intersection, he must be especially careful and look at the sign posted at the intersection. The intersection can only be crossed after there are no obstacles to do so. Next, the driver must turn on the turn signal and perform the maneuver.
General travel rules
At a T-intersection, the same rules apply as at a regular intersection; at it you can make right and left turns, as well as a U-turn.
- A right turn is made from the extreme right position on the road; you must also turn into the right lane.
- A left turn is made into any lane convenient for the driver from the left lane.
- A turn is also carried out from the extreme left position, and the width of the road must be taken into account. At some intersections there is too little room to complete a U-turn.
- At controlled intersections, difficulties rarely arise; it is enough to carefully monitor the traffic lights and markings - they provide comprehensive information about the rules of intersection. There are additional sections at the traffic light that will tell you the correct time to turn, but at the same time you need to give way to other cars that are moving towards you at that moment.
At intersections, markings called “Waffles” are often used - they are used to mark boundaries, you cannot drive beyond them, and a fine will be imposed for this.
Rules for uncontrolled T-intersections
When driving through an unregulated intersection (example: a traffic light is on standby or completely deactivated), you must follow the signs indicating priority. This situation is typical for an uncontrolled intersection, and therefore the rules for driving at an uncontrolled intersection apply. A situation where a T-shaped intersection combines unequal roads, then the most important task becomes timely determination of the road that leads to the intersection: the main one or the secondary one, and whether the main road changes its trajectory within the intersection.
Identification with the letter “T” contributes to a more convenient perception of this type of roadway: one path is represented as its core, the other as a cap or roof.
Identification of the priority as well as secondary route is prescribed in the rules for driving at an uncontrolled intersection
It is important to have quick and correct prioritization skills. The approach to the road intersection along a secondary path (often the non-priority path is the rod of the conventional letter “T” - T-shaped intersection of paths) provides travel along two possible trajectories: movement to the right or to the left
However, before entering the road intersection, you should make sure that the maneuver is safe. In particular, a specific situation obliges you to give way to vehicles that are moving with priority on the path (not the rod) on the left side, and, if it is necessary to make a left turn, also on the right.
Rules for signalized T-junctions
If the intersection is regulated by a traffic light, difficulties when moving along it are, as a rule, unlikely. Especially if this roadway is organized in the form of stripes and is indicated by markings under paragraph 1.18, as well as signs under paragraph 5.15.2 and traffic lights with an additional section. Before starting a maneuver at the intersection in the direction of the future passage, the driver’s responsibilities include changing lanes in advance to the required lane. Driving in the direction of the arrow of the additional traffic light section is only possible if the corresponding indicator is activated. When driving is carried out when a green arrow is indicated, activated together with the main red traffic light indicator, there is a need for increased vigilance, because it is imperative to give way to cars (and other vehicles) that are moving from another direction - this is exactly how this case is prescribed in the rules.