In the process of determining the amount of insurance premium under MTPL contracts, insurance companies rely on the base tariff and a set of adjustment factors. Previously, it was decided to reduce their number in 2021 to seven, eliminating two coefficients. Below we will discuss in more detail the essence and degree of influence of each of them on the final price tag.
Table of coefficients in the MTPL policy 2021
TB - Basic rate
This is the foundation of the entire calculation. Insurers have significant opportunities to maneuver the size of the base rate, choosing values within the tariff corridor established for them by the Central Bank of Russia. For 2021, for passenger vehicles owned by citizens, the selected values should be within the range of 2471-5436 rubles.
KBM – bonus-malus coefficient
The coefficient has the greatest impact on the insurance price tag, since its range of indicators varies between 0.5-2.45. The size of the coefficient depends on the level of driving accidents, and for each year spent without an accident (due to the driver’s fault), the BMR decreases by 0.05.
A complete table of existing values is presented below.
Each driver can find out their own KBM independently in real time by entering personal data on the page dedicated to the KBM coefficient.
KVS – age and length of service coefficient
The existence of this coefficient is intended to differentiate the price of compulsory motor liability insurance in accordance with the risks of an accident. The older a person is and the longer his driving experience, the less likely he is to be involved in emergency situations and the lower the value of the FAC coefficient in 2021. Young people with minimal experience will have to pay the most.
CT – territory coefficient
Introduces a gradation of cost depending on the level of accidents not only in a specific region, but also in individual settlements. This is one of the most controversial coefficients, the possibility of canceling it has been considered several times, but it continues to exist. The limit of values for it is 0.64-1.99. The full list of values can be seen on the KT 2021 odds page.
KM – vehicle power factor
Another controversial indicator that establishes the relationship between the power of a car’s engine and the insurance price tag. Possible coefficient values are 0.6-1.6. However, to receive a discount you must have a car with an engine of less than 50 hp. Even for standard Zhiguli cars an increasing factor of 1.1 is used. A complete table of existing KM values is presented below.
KO - Restriction coefficient
It affects the cost of insurance only in situations where the policyholder chooses an unlimited policy, that is, absolutely any driver is able to drive a car throughout the entire term of the contract. In this case, the increasing value of 1.94 is applied. If we are talking about cars registered to an organization, it is slightly higher – 1.97.
When including specific persons in the policy, the coefficient value is taken equal to 1.
KS - insurance duration coefficient
When applying for compulsory motor liability insurance, the policyholder is not required to enter into a contract for 12 months. The insurance can cover a shorter period, but not less than three months. In this case, the coefficient KS is applied.
Its values are presented in the list below, and the size of the reduction in the cost of insurance is not proportional to the reduction in the insurance period.
- 3 months: 0.5
- 4 months: 0.6
- 5 months: 0.65
- 6 months: 0.7
- 7 months: 0.8
- 8 months: 0.9
- 9 months: 0.95
- 10 or more months: 1
KP – insurance duration coefficient for foreign citizens
This coefficient applies only to cars that do not have registration in the Russian Federation. In this case, it acts as a substitute for the KS value. Taking into account the possibility of a short-term stay of foreign cars in Russia, the minimum insurance period is only 5 days. A complete list of coefficient values depending on the period of registration of compulsory motor liability insurance is presented below:
- 5 – 15 days: 02
- 16 days - 1 month: 0.3
- up to 2 months: 0.4
- up to 3 months: 0.5
- up to 4 months: 0.6
- up to 5 months: 0.65
- up to 6 months: 0.7
- up to 7 months: 0.8
- up to 8 months: 0.9
- up to 9 months: 0.95
- up to 10 months or more: 1
Basic rates for compulsory motor liability insurance from January 9, 2021
Everything is quite simple here.
The insurer sets the basic rates within the minimum and maximum limits itself. The principle by which this is done remains unknown. More likely. The make and age of the car, region, as well as the insurance history of the car owner are taken into account. In practice, for such a short time (since January 9 of this year), for example, for passenger cars of category B owned by individuals, the maximum value of 4,942 rubles is used. This conclusion was made experimentally, namely when trying to buy an electronic MTPL policy from a number of popular insurance companies. Now it’s worth considering the basic tariffs.
The insurer must notify the Bank of Russia in writing about the established base rate within three working days from the date of its confirmation. He should also add this information to the official website.
Table of base rates 2021 by vehicle category
| № | Type (category) and purpose of the vehicle | Basic insurance rate (rubles) | |
| Minimum TB value | Maximum TB value | ||
| 1. | Motorcycles, mopeds and light quadricycles (vehicles of categories “A”, “M”) | 694 | 1 407 |
| 2. | Vehicles of categories “B”, “BE” | ||
| 2.1 | legal entities | 2 058 | 2 911 |
| 2.2 | individuals, individual entrepreneurs | 2 746 | 4 942 |
| 2.3 | used as a taxi | 4 110 | 7 399 |
| 3. | Vehicles of categories “C” and “CE” | ||
| 3.1 | with a permissible maximum weight of up to 16 tons. | 2 807 | 5 053 |
| 3.2 | with a permissible maximum weight of more than 16 tons. | 4 227 | 7 609 |
| 4. | Vehicles of categories “D” and “DE” | ||
| 4.1 | with a number of passenger seats up to 16 | 2 246 | 4 044 |
| 4.2 | with more than 16 passenger seats | 2 807 | 5 053 |
| 4.3 | used for regular transportation with pick-up and disembarkation of passengers both at established stopping points along the regular transportation route, and in any place not prohibited by traffic rules along the regular transportation route | 4 110 | 7 399 |
| 5. | Trolleybuses (vehicles of category “Tb”) | 2 246 | 4 044 |
| 6. | Trams (vehicles of category "Tm") | 1 401 | 2 521 |
| 7. | Tractors, self-propelled road-building and other machines, with the exception of vehicles that do not have wheeled propulsion systems | 899 | 1 895 |
To determine the category of a vehicle, the data noted in the document on its registration is used. This could be a vehicle passport, registration certificate, technical passport, technical certificate. The information provided by the policyholder when concluding the contract is also taken into account.
Rules and features
The insured is a legal entity. Therefore, the agreement is concluded by the director of the organization or an authorized representative, on the basis of an internal order of the company. The law provides that companies can obtain a compulsory motor liability insurance agreement for a period of 1 year. If the car was purchased for the purpose of driving, then you can issue a form for 14 days.
The vehicles are driven by full-time company employees. Therefore, the contract states that an unlimited number of persons are allowed to drive the vehicle. This means that employees can drive a car if they have a waybill or a special permit.
There is a list of vehicles that must be insured according to the rules. An insurance company can conclude a contract for a passenger car, truck, bus, or special equipment. A separate contract is not issued for trailers. They are an addition to the cargo vehicle, so the contract is general. It indicates that the cargo vehicle is used with a trailer.
There is a system of discounts for accident-free driving. But they are assigned not to the organization, but to the vehicle. That is, every new car has its own insurance history.
To issue a policy, a representative of the organization contacts the insurance company, having with him a complete package of documents. If there are several cars, a list of vehicles is prepared. After studying the received documents, the manager draws up an agreement. It includes insurance conditions, insurance premium and payment terms. The policyholder then receives an invoice for payment. Having a contract and paying the invoice, the company representative purchases insurance policies.
Compensation payments were previously transferred to the organizations' accounts. In 2017, a unified system for settling losses was created. This means that money is not paid to drivers. Insurance companies transfer compensation to service stations that repair cars (you can find out how the cost of car repairs is calculated under compulsory motor liability insurance here).
Important! The MTPL insurance limit for legal entities is always set for each individual accident case, and is not extended over a year. This is very convenient because the company does not need to enter into a new contract after each accident.
The compulsory insurance rules contain a complete list of documents that the company must provide:
- Vehicle passport.
- Vehicle registration certificate.
- Technical inspection for each car.
- Requisites.
- Certificate of registration of a legal entity.
- Power of attorney (if necessary).
- Company INN.
- Application for insurance in the appropriate form.
Sometimes insurance companies fill out the applications themselves. All the organization has to do is sign. This is a common practice if many cars are insured at once or the policyholder is a VIP client.
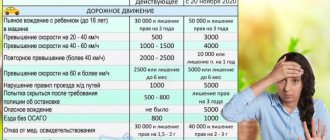
Penalties for the lack of compulsory state MTPL insurance apply to both individuals and legal entities. The following are the fine amounts:
- The driver drives a vehicle without an insurance policy - 500 rubles.
- If the driver handed over control to a person who does not have a driver’s license - 3,000 rubles.
- When using a vehicle after the expiration of the insurance period - 500 rubles.
- If the owner of the car obviously does not have an insurance policy - 800 rubles.
OSAGO coefficients from January 9, 2021
Dear readers!
Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please contact the online consultant form
It's fast and free!
Or call us by phone (24/7):
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, call us by phone. It's fast and free!
What else to read:
- My car was scratched in the yard, what should I do?
- Europrotocol 2021
- How to get money instead of repairs under compulsory motor liability insurance: a detailed review
+7 (495) 980-97-90(ext.589) Moscow,
Moscow region
+8 (812) 449-45-96(ext.928) St. Petersburg,
Leningrad region
+8 (800) 700-99-56 (ext. 590) Regions
(free call for all regions of Russia)
The amount of the insurance premium that is payable in accordance with the contract (policy price) is calculated by multiplying different coefficients. For example, if you take cars from categories B and BE, the insurance price will include the following components:
- Basic tariff (TB).
- Territorial coefficient (CT). Determined based on the region in which the machine is primarily used.
- Bonus-malus ratio (BMR). This coefficient takes into account the presence or absence of insurance payments made by insurance companies previously.
- Age-experience coefficient (AEC). A coefficient determined taking into account the driver’s age and experience.
- Limiting factor (CL). Determined taking into account the availability of data on the number of drivers who can drive the car.
- Engine power factor (PM). It is calculated taking into account the engine power of the machine.
- Seasonality coefficient (SC). Takes into account the seasonality of vehicle operation.
- Violation rate (CN).
Insurance coefficients for road accidents
The country's legislative bodies provide a set of coefficients for road accidents. They are divided into two groups:
Attention! If you have any questions, you can chat for free with a lawyer at the bottom of the screen or call Moscow; Saint Petersburg; Free call for all of Russia.
- fining;
- encouraging.
The first group includes coefficients created to increase responsibility among careless drivers who ignore the rules. Their task is to encourage a person to drive correctly by withdrawing additional money from him.
The second group includes coefficients intended for drivers who, on the contrary, comply with traffic rules. For careful driving, a person receives additional bonuses.
Both groups have the same goal - to reduce the number of accidents. There are three main MTPL increasing coefficients used in the event of accidents:
- Kt - depends on the average accident rate in the locality in which the owner of the vehicle lives (in most cases, for residents of small towns it is lower, which means they will have to pay less for an MTPL insurance policy);
- Kn - determined on the basis of compliance with the rules provided for in the insurance contract - if the driver violated them (as a result of which an accident occurred, or the scene of the accident was left), the cost of the policy increases;
- Kvs - depends on how old the car owner is and how much driving experience he has (the older the driver, the lower the price for obtaining compulsory motor liability insurance will be for him).
- KBM - depends on the number of accidents committed by the driver.
- KN – coefficient of traffic violations.
- KM – engine power factor. Measured in horsepower.
The Kbm coefficient is also important for issuing an MTPL insurance policy. It is associated with the rate of accidents on highways.
Territorial coefficient
This coefficient or the territory of primary use of the car is determined taking into account the place of residence of the car owner indicated in the car’s passport, vehicle registration certificate, and in the driver’s passport. For legal entities, it is determined by the direct location of the legal entity, its branch or representative office, noted in the constituent documentation.
If the car owner permanently lives abroad and temporarily operates the car in the Russian Federation, a CT size of 1,7.
Table
You can use filtering in the table. In the search field of the 2nd column (Territory of preferential use of transport proximity), enter your region to quickly find out the coefficient.
| № | Territory of primary use of vehicles | CT coefficient for vehicles, with the exception of tractors, self-propelled road construction and other machines | CT coefficient for tractors, self-propelled road-building and other machines, with the exception of vehicles that do not have wheel propulsors |
| 1 | Republic of Adygea | 1,3 | 1 |
| 2 | Altai Republic | ||
| 2.1 | Gorno-Altaisk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 2.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 3 | Republic of Bashkortostan | ||
| 3.1 | Blagoveshchensk, Oktyabrsky | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 3.2 | Ishimbay, Kumertau, Salavat | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 3.3 | Sterlitamak, Tuymazy | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 3.4 | Ufa | 1,8 | 1 |
| 3.5 | Other cities and towns | 1 | 0,8 |
| 4 | The Republic of Buryatia | ||
| 4.1 | Ulan-Ude | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 4.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 5 | The Republic of Dagestan | ||
| 5.1 | Buynaksk, Derbent, Kaspiysk, Makhachkala, Khasavyurt | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 5.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 6 | The Republic of Ingushetia | ||
| 6.1 | Malgobek | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 6.2 | Nazran | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 6.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 7 | Kabardino-Balkarian Republic | ||
| 7.1 | Nalchik, Prokhladny | 1 | 0,8 |
| 7.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 8 | Republic of Kalmykia | ||
| 8.1 | Elista | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 8.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 9 | Karachay-Cherkess Republic | 1 | 0,8 |
| 10 | Republic of Karelia | ||
| 10.1 | Petrozavodsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 10.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 11 | Komi Republic | ||
| 11.1 | Syktyvkar | 1,6 | 1 |
| 11.2 | Ukhta | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 11.3 | Other cities and towns | 1 | 0,8 |
| 12 | Republic of Crimea | ||
| 12.1 | Simferopol | 0,6 | 0,6 |
| 12.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,6 |
| 13 | Mari El Republic | ||
| 13.1 | Volzhsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 13.2 | Yoshkar-Ola | 1,4 | 0,8 |
| 13.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 14 | The Republic of Mordovia | ||
| 14.1 | Ruzaevka | 1,2 | 1 |
| 14.2 | Saransk | 1,5 | 1 |
| 14.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,6 |
| 15 | The Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) | ||
| 15.1 | Neryungri | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 15.2 | Yakutsk | 1,2 | 0,7 |
| 15.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 16 | Republic of North Ossetia-Alania | ||
| 16.1 | Vladikavkaz | 1 | 0,8 |
| 16.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 17 | Republic of Tatarstan | ||
| 17.1 | Almetyevsk, Zelenodolsk, Nizhnekamsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 17.2 | Bugulma, Leninogorsk, Chistopol | 1 | 0,8 |
| 17.3 | Elabuga | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 17.4 | Kazan | 2 | 1,2 |
| 17.5 | Naberezhnye Chelny | 1,7 | 1 |
| 17.6 | Other cities and towns | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 18 | Tyva Republic | ||
| 18.1 | Kyzyl | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 18.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 19 | Udmurt republic | ||
| 19.1 | Votkinsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 19.2 | Glazov, Sarapul | 1 | 0,8 |
| 19.3 | Izhevsk | 1,6 | 1 |
| 19.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 20 | The Republic of Khakassia | ||
| 20.1 | Abakan, Sayanogorsk, Chernogorsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 20.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 21 | Chechen Republic | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 22 | Chuvash Republic | ||
| 22.1 | Kanash | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 22.2 | Novocheboksarsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 22.3 | Cheboksary | 1,7 | 1 |
| 22.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 23 | Altai region | ||
| 23.1 | Barnaul | 1,7 | 1 |
| 23.2 | Biysk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 23.3 | Zarinsk, Novoaltaisk, Rubtsovsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 23.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 24 | Transbaikal region | ||
| 24.1 | Krasnokamensk | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 24.2 | Chita | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 24.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 25 | Kamchatka Krai | ||
| 25.1 | Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky | 1,3 | 1 |
| 25.2 | Other cities and towns | 1 | 0,6 |
| 26 | Krasnodar region | ||
| 26.1 | Anapa, Gelendzhik | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 26.2 | Armavir, Sochi, Tuapse | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 26.3 | Belorechensk, Yeisk, Kropotkin, Krymsk, Kurganinsk, Labinsk, Slavyansk-on-Kuban, Timashevsk, Tikhoretsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 26.4 | Krasnodar, Novorossiysk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 26.5 | Other cities and towns | 1 | 0,8 |
| 27 | Krasnoyarsk region | ||
| 27.1 | Achinsk, Zelenogorsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 27.2 | Zheleznogorsk, Norilsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 27.3 | Kansk, Lesosibirsk, Minusinsk, Nazarovo | 1 | 0,8 |
| 27.4 | Krasnoyarsk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 27.5 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 28 | Perm region | ||
| 28.1 | Berezniki, Krasnokamsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 28.2 | Lysva, Tchaikovsky | 1 | 0,8 |
| 28.3 | Permian | 2 | 1,2 |
| 28.4 | Solikamsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 28.5 | Other cities and towns | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 29 | Primorsky Krai | ||
| 29.1 | Arsenyev, Artem, Nakhodka, Spassk-Dalniy, Ussuriysk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 29.2 | Vladivostok | 1,4 | 1 |
| 29.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 30 | Stavropol region | ||
| 30.1 | Budennovsk, Georgievsk, Essentuki, Mineralnye Vody, Nevinnomyssk, Pyatigorsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 30.2 | Kislovodsk, Mikhailovsk, Stavropol | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 30.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 31 | Khabarovsk region | ||
| 31.1 | Amursk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 31.2 | Komsomolsk-on-Amur | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 31.3 | Khabarovsk | 1,7 | 1 |
| 31.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 32 | Amur region | ||
| 32.1 | Belogorsk, Svobodny | 1,1 | 0,9 |
| 32.2 | Blagoveshchensk | 1,6 | 0,9 |
| 32.3 | Other cities and towns | 1 | 0,6 |
| 33 | Arhangelsk region | ||
| 33.1 | Arkhangelsk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 33.2 | Kotlas | 1,6 | 1 |
| 33.3 | Severodvinsk | 1,7 | 1 |
| 33.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,85 | 0,5 |
| 34 | Astrakhan region | ||
| 34.1 | Astrakhan | 1,4 | 1 |
| 34.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 35 | Belgorod region | ||
| 35.1 | Belgorod | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 35.2 | Gubkin, Stary Oskol | 1 | 0,8 |
| 35.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 36 | Bryansk region | ||
| 36.1 | Bryansk | 1,5 | 1 |
| 36.2 | Klintsy | 1 | 0,8 |
| 36.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 37 | Vladimir region | ||
| 37.1 | Vladimir | 1,6 | 1 |
| 37.2 | Gus-Khrustalny | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 37.3 | Moore | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 37.4 | Other cities and towns | 1 | 0,8 |
| 38 | Volgograd region | ||
| 38.1 | Volgograd | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 38.2 | Volzhsky | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 38.3 | Kamyshin, Mikhailovka | 1 | 0,8 |
| 38.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 39 | Vologda Region | ||
| 39.1 | Vologda | 1,7 | 1 |
| 39.2 | Cherepovets | 1,8 | 1 |
| 39.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 40 | Voronezh region | ||
| 40.1 | Borisoglebsk, Liski, Rossosh | 1,1 | 0,9 |
| 40.2 | Voronezh | 1,5 | 1,1 |
| 40.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,6 |
| 41 | Ivanovo region | ||
| 41.1 | Ivanovo | 1,8 | 1 |
| 41.2 | Kineshma | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 41.3 | Shuya | 1 | 0,8 |
| 41.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 42 | Irkutsk region | ||
| 42.1 | Angarsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 42.2 | Bratsk, Tulun, Ust-Ilimsk, Ust-Kut, Cheremkhovo | 1 | 0,8 |
| 42.3 | Irkutsk | 1,7 | 1 |
| 42.4 | Usolye-Sibirskoye | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 42.5 | Shelekhov | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 42.6 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 43 | Kaliningrad region | ||
| 43.1 | Kaliningrad | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 43.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 44 | Kaluga region | ||
| 44.1 | Kaluga | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 44.2 | Obninsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 44.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 45 | Kemerovo region | ||
| 45.1 | Anzhero-Sudzhensk, Kiselevsk, Yurga | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 45.2 | Belovo, Berezovsky, Mezhdurechensk, Osinniki, Prokopyevsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 45.3 | Kemerovo | 1,9 | 1 |
| 45.4 | Novokuznetsk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 45.5 | Other cities and towns | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 46 | Kirov region | ||
| 46.1 | Kirov | 1,4 | 1 |
| 46.2 | Kirovo-Chepetsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 46.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 47 | Kostroma region | ||
| 47.1 | Kostroma | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 47.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 48 | Kurgan region | ||
| 48.1 | Mound | 1,4 | 0,8 |
| 48.2 | Shadrinsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 48.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 49 | Kursk region | ||
| 49.1 | Zheleznogorsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 49.2 | Kursk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 49.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 50 | Leningrad region | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 51 | Lipetsk region | ||
| 51.1 | Dace | 1 | 0,8 |
| 51.2 | Lipetsk | 1,5 | 1 |
| 51.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 52 | Magadan Region | ||
| 52.1 | Magadan | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 52.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 53 | Moscow region | 1,7 | 1 |
| 54 | Murmansk region | ||
| 54.1 | Apatity, Monchegorsk | 1,3 | 1 |
| 54.2 | Murmansk | 2,1 | 1,2 |
| 54.3 | Severomorsk | 1,6 | 1 |
| 54.4 | Other cities and towns | 1,2 | 1 |
| 55 | Nizhny Novgorod Region | ||
| 55.1 | Arzamas, Vyksa, Sarov | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 55.2 | Balakhna, Bor, Dzerzhinsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 55.3 | Kstovo | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 55.4 | Nizhny Novgorod | 1,8 | 1 |
| 55.5 | Other cities and towns | 1 | 0,8 |
| 56 | Novgorod region | ||
| 56.1 | Borovichi | 1 | 0,8 |
| 56.2 | Velikiy Novgorod | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 56.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 57 | Novosibirsk region | ||
| 57.1 | Berdsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 57.2 | Iskitim | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 57.3 | Kuibyshev | 1 | 0,8 |
| 57.4 | Novosibirsk | 1,7 | 1 |
| 57.5 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 58 | Omsk region | ||
| 58.1 | Omsk | 1,6 | 1 |
| 58.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 59 | Orenburg region | ||
| 59.1 | Buguruslan, Buzuluk, Novotroitsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 59.2 | Orenburg | 1,7 | 1 |
| 59.3 | Orsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 59.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 60 | Oryol Region | ||
| 60.1 | Livny, Mtsensk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 60.2 | Eagle | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 60.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 61 | Penza region | ||
| 61.1 | Zarechny | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 61.2 | Kuznetsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 61.3 | Penza | 1,4 | 1 |
| 61.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 62 | Pskov region | ||
| 62.1 | Velikie Luki | 1 | 0,8 |
| 62.2 | Pskov | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 62.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 63 | Rostov region | ||
| 63.1 | Azov | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 63.2 | Bataysk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 63.3 | Volgodonsk, Gukovo, Kamensk-Shakhtinsky, Novocherkassk, Novoshakhtinsk, Salsk, Taganrog | 1 | 0,8 |
| 63.4 | Rostov-on-Don | 1,8 | 1 |
| 63.5 | Mines | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 63.6 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 64 | Ryazan Oblast | ||
| 64.1 | Ryazan | 1,4 | 1 |
| 64.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 65 | Samara Region | ||
| 65.1 | Novokuybyshevsk, Syzran | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 65.2 | Samara | 1,6 | 1 |
| 65.3 | Tolyatti | 1,5 | 1 |
| 65.4 | Chapaevsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 65.5 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 66 | Saratov region | ||
| 66.1 | Balakovo, Balashov, Volsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 66.2 | Saratov | 1,6 | 1 |
| 66.3 | Engels | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 66.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 67 | Sakhalin region | ||
| 67.1 | Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | 1,5 | 1 |
| 67.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 68 | Sverdlovsk region | ||
| 68.1 | Asbest, Revda | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 68.2 | Berezovsky, Verkhnyaya Pyshma, Novouralsk, Pervouralsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 68.3 | Verkhnyaya Salda, Polevskoy | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 68.4 | Ekaterinburg | 1,8 | 1 |
| 68.5 | Other cities and towns | 1 | 0,8 |
| 69 | Smolensk region | ||
| 69.1 | Vyazma, Roslavl, Safonovo, Yartsevo | 1 | 0,8 |
| 69.2 | Smolensk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 69.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 70 | Tambov Region | ||
| 70.1 | Michurinsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 70.2 | Tambov | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 70.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 71 | Tver region | ||
| 71.1 | Vyshny Volochek, Kimry, Rzhev | 1 | 0,8 |
| 71.2 | Tver | 1,5 | 1 |
| 71.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 72 | Tomsk region | ||
| 72.1 | Seversk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 72.2 | Tomsk | 1,6 | 1 |
| 72.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 73 | Tula region | ||
| 73.1 | Aleksin, Efremov, Novomoskovsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 73.2 | Tula | 1,5 | 1 |
| 73.3 | Uzlovaya, Shchekino | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 73.4 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 74 | Tyumen region | ||
| 74.1 | Tobolsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 74.2 | Tyumen | 2 | 1,2 |
| 74.3 | Other cities and towns | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 75 | Ulyanovsk region | ||
| 75.1 | Dimitrovgrad | 1,2 | 0,9 |
| 75.2 | Ulyanovsk | 1,5 | 1,1 |
| 75.3 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,6 |
| 76 | Chelyabinsk region | ||
| 76.1 | Zlatoust, Miass | 1,4 | 0,8 |
| 76.2 | Kopeisk | 1,6 | 1 |
| 76.3 | Magnitogorsk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 76.4 | Satka, Chebarkul | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 76.5 | Chelyabinsk | 2,1 | 1,3 |
| 76.6 | Other cities and towns | 1 | 0,8 |
| 77 | Yaroslavl region | ||
| 77.1 | Yaroslavl | 1,5 | 1 |
| 77.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 78 | Moscow | 2 | 1,2 |
| 79 | Saint Petersburg | 1,8 | 1 |
| 80 | Sevastopol | 0,6 | 0,6 |
| 81 | Jewish Autonomous Region | ||
| 81.1 | Birobidzhan | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 81.2 | Other cities and towns | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 82 | Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 83 | Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra | ||
| 83.1 | Kogalym | 1 | 0,8 |
| 83.2 | Nefteyugansk, Nyagan | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 83.3 | Surgut | 2 | 1,2 |
| 83.4 | Nizhnevartovsk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 83.5 | Khanty-Mansiysk | 1,5 | 1 |
| 83.6 | Other cities and towns | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 84 | Chukotka Autonomous Okrug | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 85 | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | ||
| 85.1 | New Urengoy | 1 | 0,8 |
| 85.2 | Noyabrsk | 1,7 | 1 |
| 85.3 | Other cities and towns | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 86 | Baikonur | 0,6 | 0,5 |
Registration online
Not all managers can allocate time in their schedule to personally arrange insurance, and transferring authority is not always convenient or possible. Problems may arise when the nearest insurance company office is tens or hundreds of kilometers away. An electronic policy system has been developed especially for such cases.
To apply for compulsory motor liability insurance online, you need to complete the following steps:
- Select an insurer and go to the official website.
- Please register. You need to come up with (or they will give you) a login and password for authorization.
- Log in to your personal account and fill out the company details.
- Fill out the electronic application. You must first calculate the cost of the policy (manually or through an online calculator).
- Scan the documents required for registration and upload them to the site.
- Submit an application for registration to the RSA. If errors are found, you will receive an appropriate response and the opportunity to resubmit your application. The check takes about 40 minutes.
- After registering, pay for the policy.
- After payment you will receive an MTPL insurance policy form by email. It must be printed and stored in the vehicle.
Many people ask the question, is such an ordinary printout on a printer considered valid and legal? It can be easily forged, but when checking corporate compulsory motor liability insurance, traffic police officers use the RSA electronic database, where they check its validity using the registration number of the document.
Bonus-malus coefficient
KBM is an insurance tariff coefficient, which is determined taking into account whether payments were made by insurers in the period from April 1 of the previous year to March 31 of the next year. Simply put, its size will depend on whether the policyholder was at fault for the accident or not.
For example, this year the BMR is 1. Next year it will be equal to 0.95, provided that the driver is not the culprit of the traffic accident. Accordingly, the policy will be cheap. If the driver causes one accident, in the next year this coefficient for him will be equal to 1.55, if two accidents, then 2.45, etc. This will make insurance more expensive.
Table
| Class when taking out annual insurance | Coefficient | Class at the end of the annual insurance, taking into account all insurance situations for the entire period of validity of the MTPL contracts | Year | Price | ||||
| 0 payouts | 1 payment | 2 payments | 3 payments | more than 3 payments | ||||
| M | 2,45 | 0 | M | M | M | M | ||
| 0 | 2,3 | 1 | M | M | M | M | ||
| 1 | 1,55 | 2 | M | M | M | M | ||
| 2 | 1,4 | 3 | 1 | M | M | M | ||
| 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | M | M | M | ||
| 4 | 0.95 | 5 | 2 | 1 | M | M | ||
| 5 | 0.9 | 6 | 3 | 1 | M | M | ||
| 6 | 0.85 | 7 | 4 | 2 | M | M | ||
| 7 | 0.8 | 8 | 4 | 2 | M | M | ||
| 8 | 0.75 | 9 | 5 | 2 | M | M | ||
| 9 | 0.7 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 1 | M | ||
| 10 | 0.65 | 11 | 6 | 3 | 1 | M | ||
| 11 | 0.6 | 12 | 6 | 3 | 1 | M | ||
| 12 | 0.55 | 13 | 6 | 3 | 1 | M | ||
| 13 | 0.5 | 13 | 7 | 3 | 1 | M | ||
How to determine PIC with unlimited insurance
Unlimited or open insurance is the ability to include an unlimited number of persons in the policy. When it is completed, a mark is placed on the conclusion of an agreement for an indefinite number of drivers. In the line about those allowed to drive or where the license number is written, there will be a dash; even the owner of the vehicle will not be indicated.
The unlimited policy coefficient in the current year is 1.87, and the FAC is 1.
To save money, it is more profitable for young and inexperienced drivers to take out open insurance . The coefficient will decrease, for example, from 1.95 to 1.87.
Accordingly, there is no need to determine the PIC for this type of insurance; it is fixed, its value is equal to 1.
The open option is convenient for owners of taxi and bus services, where drivers change frequently. If you practice entrusting your personal car to friends and acquaintances, but at the date of registration of the policy you do not know who exactly, this service option is also suitable for you.
Age-experience coefficient
This coefficient determines insurance rates taking into account how old the driver is and how long a driving experience he has. As already mentioned, from January 9 the number of steps increased from 4 to 58.
Table
| № | Experience, years\Age, years | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3-4 | 5-6 | 7-9 | 10-14 | 14+ |
| 1 | 16 — 21 | 1,87 | 1,87 | 1,87 | 1,66 | 1,66 | |||
| 2 | 22 — 24 | 1,77 | 1,77 | 1,77 | 1,04 | 1,04 | 1,04 | ||
| 3 | 25 — 29 | 1,77 | 1,69 | 1,63 | 1,04 | 1,04 | 1,04 | 1,01 | |
| 4 | 30 — 34 | 1,63 | 1,63 | 1,63 | 1,04 | 1,04 | 1,01 | 0,96 | 0,96 |
| 5 | 35 — 39 | 1,63 | 1,63 | 1,63 | 0,99 | 0,96 | 0,96 | 0,96 | 0,96 |
| 6 | 40 — 49 | 1,63 | 1,63 | 1,63 | 0,96 | 0,96 | 0,96 | 0,96 | 0,96 |
| 7 | 50 — 59 | 1,63 | 1,63 | 1,63 | 0,96 | 0,96 | 0,96 | 0,96 | 0,96 |
| 8 | over 59 | 1,6 | 1,6 | 1,6 | 0,93 | 0,93 | 0,93 | 0,93 | 0,93 |
If the car is registered in another country and is temporarily used in the Russian Federation, then the FAC is determined in the following dimensions:
- 1.7 – for a car owned by an individual;
- 1 – for a car that is the property of a legal entity.
How to calculate the indicator
Calculating the indicator for each participant is very simple. To do this you should:
- select the age of the traffic participant in the column;
- in the line, select how many years the vehicle has been driven by license;
- look at the coefficient at the intersection of two indicators.
An example of calculating the FAC according to the table.
For example, a 35-year-old driver with 7 years of experience is admitted. When calculating compulsory motor insurance for such a motorist, a tariff of 0.96 will be taken into account.
Important! If the liability of several drivers is insured under compulsory motor liability insurance (their number cannot exceed 5 people), then the coefficient is determined for each. As a result, the maximum value is used for calculation. For example, two drivers are allowed to drive a car. The first has age and experience of 57/20 years, and the second has 20/1. The calculation will take into account the tariff of 1.87, which corresponds to the second participant in the movement.
Online calculation
For convenience, we have made a cool OSAGO calculator, in which you can immediately see all the coefficients of the insurance policy.
Thanks to this, you can quickly find out the value of the indicator and not have to delve into what it is and how to do the calculation yourself using the table.
Limiting factor
The CO is determined taking into account the number of persons allowed to drive in accordance with the policy. That is, whether the control of the car is entrusted to a limited or an unlimited number of drivers.
Table
| № | Information on the number of persons allowed to drive a vehicle owned by an individual | KO coefficient |
| 1 | The compulsory insurance contract provides for a limitation on the number of persons allowed to drive a vehicle | 1 |
| 2 | The compulsory insurance contract does not provide for a limitation on the number of persons allowed to drive a vehicle | 1,87 |
For legal entities this indicator is 1.8
What is KVS
When calculating compulsory motor liability insurance, the age and length of service coefficient of each driver who is allowed to drive a car is used. In January 2021, amendments were made to the tariff manual. As a result of innovations, the ranges according to motorists were increased.
Thanks to the new tariffs, experienced drivers received 7% discounts on MTPL for driving experience.
Within the framework of the tariffs that were in force until January 2021, the minimum coefficient for fuel consumption was one. According to the new rules, its value is reduced to 0.93, which gives an additional discount on the policy of 7%.
Engine power factor
To obtain data on the engine power of a car, STS or PTS is used. If these papers do not contain this data, information is taken from manufacturers’ catalogs and other official sources. If the PTS indicator is indicated in kilowatts, the ratio 1 kW/hour = 1.35962 hp is used to convert into horsepower.
Table
| № | Engine power (horsepower) | KM coefficient |
| 1 | Up to 50 inclusive | 0,6 |
| 2 | Over 50 to 70 inclusive | 1 |
| 3 | Over 70 to 100 inclusive | 1,1 |
| 4 | Over 100 to 120 inclusive | 1,2 |
| 5 | Over 120 to 150 inclusive | 1,4 |
| 6 | Over 150 | 1,6 |
How can I get a discount on my insurance policy?
Of course, any driver will be happy to save money. The insurance contract specifies cases when the coefficient may be reduced by several points. For driving without accidents in the past year, you can get a 5% discount . As a result, the more years there are no traffic accidents, the stronger the discount percentage will be and the CBM coefficient will decrease. But when buying a new car, a similar discount remains.
What could be the biggest discount on an MTPL policy? The maximum discount for trouble-free operation can reach 50%. But to achieve it, the driver must drive conscientiously for more than 10 years. A word of caution here—some unscrupulous insurers think otherwise. You can often see minibuses and stationary trailers near the MREO, offering compulsory motor liability insurance policies with a discount of up to 40%. It is important to understand here - this is not according to the law!
When a new compulsory insurance contract (AIC) is concluded or an existing one is extended, the insurer must check the loss-worthiness of all drivers included in the policy using a common information system. Of course, the intermediary insurer simply cannot provide the discount it claims legally. Most often, the MTPL policy of a bankrupt company is simply sold, or even a completely fake one. No insurance company will pay under such a policy, and compensation for the damage caused will only be the responsibility of the person responsible for the traffic accident.
Seasonality factor
This indicator depends on how many months out of 12 the driver will use the car.
Table
| № | Period of use of the vehicle | KS coefficient |
| 1 | 3 months | 0,5 |
| 2 | 4 months | 0,6 |
| 3 | 5 months | 0,65 |
| 4 | 6 months | 0,7 |
| 5 | 7 months | 0,8 |
| 6 | 8 months | 0,9 |
| 7 | 9 months | 0,95 |
| 8 | 10 months or more | 1 |
How does the coefficient increase?
The increase in the MTPL coefficient after an accident depends on the exact number of road accidents that the car owner encountered during the period of validity of the insurance policy. Each situation is considered individually by a special commission of the insurance company, guided by the Civil Code of Russia. The insurer is obliged to act on the basis of federal laws 4015-1 and. If laws are violated, the car owner has the right to go to court and demand compensation for damages. At the same time, he must provide evidence confirming his words.
The increase in the MTPL coefficient after an accident depends on how much a person uses the services of a particular insurance company. For inexperienced drivers of the standard class who have recently taken out insurance, a strict control system is provided:
- after one accident, the driver receives first class (increasing compulsory motor vehicle liability insurance coefficient is lower than standard);
- The car owner’s KBM becomes equal to the value “1.55”;
- issuing an insurance policy costs almost half as much.
If two or more accidents occur, the driver’s class is marked with the value “M”. The MTPL coefficient for this class becomes “2.45”. The next time you pay, the price for insurance will be 145% higher than the standard one.
The scheme for drivers who have been using the services of an insurer for a long time is less stringent. If an insured event occurs after an accident, the increase in the KBM OSAGO will only affect the discount accrued for a year of impeccable driving. A driver with ten years of accident-free driving experience would have to be involved in three accidents in a row to reach the standard level.
It should be borne in mind that when changing the coefficient, the number of accidents over the entire period of use of the insurance policy is taken into account, and not one per year.
Violation rate
This coefficient is used in the presence of action or inaction of the car owner, provided for in clause 3 of article 9 of the Federal Law “On Compulsory Motor Liability Insurance”.
This coefficient will be used and amount to 1.5 if the owner of the car:
- Provided the insurance company with deliberately untrue information about the requested circumstances affecting the amount of the insurance premium under the contract, due to which it was paid in a lesser amount than what should have been paid if the truthful information was provided.
- Knowingly contributed to the occurrence of an insured event or the associated losses to increase, or deliberately distorted the circumstances of its occurrence in order to increase the amount of compensation.
- Provoked harm under circumstances that are the basis for a claim of recourse.
Increasing coefficient for compulsory motor third party liability insurance after an accident
Regardless of qualifications, when receiving an insurance policy, the driver is issued a third level class. Every year when you renew your insurance, it gradually increases by one value. So, in order to obtain a thirteenth level class, the car owner must renew the OSAGO policy for ten years.
But such development is only possible if during the specified period the person has never been involved in an accident. Careful drivers receive a 5% discount from the insurer for each incident-free year. Accordingly, after a ten-year period, drivers who have not been involved in an accident receive a 50% discount on insurance.
But it will be immediately reduced if the driver gets into an accident at least once. The car owner's rating is also automatically lowered. Depending on the number of insured events, the level decreases from two to seven values. The more often a person gets into an accident, the lower the insurer’s trust in him.
When the OSAGO class after an accident falls below the third level, the driver begins to accrue penalties in the form of inflated tariffs. The level does not drop below class “M”. It will take at least four years of accident-free driving to return to normal.
Trailer availability factor
The CPR is determined depending on whether the contract contains information that makes it possible to operate the car together with its trailer.
Table
| № | Trailer depending on the type and purpose of the vehicle | KPR coefficient |
| 1 | Trailers for cars owned by legal entities, motorcycles and scooters | 1,16 |
| 2 | Trailers for trucks with a permissible maximum weight of 16 tons or less, semi-trailers, trailers | 1,4 |
| 3 | Trailers for trucks with a permissible maximum weight of more than 16 tons, semi-trailers, trailers | 1,25 |
| 3 | Trailers for tractors, self-propelled road construction and other machines, with the exception of vehicles that do not have wheeled propulsion devices | 1,24 |
| 4 | Trailers for other types (categories) and purpose of vehicles | 1 |
How can the OSAGO coefficient change?
The MTPL coefficient, depending on the driving quality of the vehicle owner after an accident, can:
- rise;
- go down;
- remain unchanged.
If the driver does not get into an accident, after a certain period the MTPL coefficient will begin to increase. If a person often encounters road accidents, this indicator, on the contrary, will decrease. This scheme is quite simple, but there are cases in which the coefficient remains stable.
The MTPL increasing coefficient does not change after registration of an accident if:
- insurance was issued for the trailer, and not for the car;
- the car was involved in an accident, but the policy was issued for a period of no more than one year;
- transit type transport was provided with insurance.
Also, the system does not apply to foreigners. Under other conditions, the OSAGO coefficient after an accident changes in the standard way.
Insurance period or term coefficient
This coefficient (CP) depends on the duration of the insurance.
Table
| № | Insurance period for compulsory civil liability insurance of owners of vehicles registered in foreign countries and temporarily used on the territory of the Russian Federation | KP coefficient |
| 1 | From 5 to 15 days | 0,2 |
| 2 | From 16 days to 1 month | 0,3 |
| 3 | 2 months | 0,4 |
| 4 | 3 months | 0,5 |
| 5 | 4 months | 0,6 |
| 6 | 5 months | 0,65 |
| 7 | 6 months | 0,7 |
| 8 | 7 months | 0,8 |
| 9 | 8 months | 0,9 |
| 10 | 9 months | 0,95 |
| 11 | 10 months or more | 1 |
How to bypass the MTPL increasing coefficient after an accident?
After the adoption of amendments to the law “On Compulsory Motor Liability Insurance”, the most reliable way to bypass the increasing coefficient is to avoid getting into an accident. Inexperienced drivers should consider a number of options that may not be possible:
- change of insurance company;
- taking out insurance for another person;
- hiding information about an accident when changing the insurance company.
The second method was the most common. This trick was used if the vehicle insurance was issued for several drivers. As noted earlier, CBM increases after an accident only for the person who was driving the car at the time of the accident. In this case, the next time the policy is renewed, it does not fit into the contract, and the OSAGO coefficient does not change. This method is easiest to implement for married couples.
Attempts to avoid changes to the KBM are monitored. Despite this, many car owners claim that they managed to clear their driving history without renewing their insurance for a year. But such cases are more likely to be an accident than a pattern. Within 15 days after the accident, the insurer enters data about the car owner into the general database. The ID number is also indicated there.
Another way to avoid changes in the increasing MTPL ratio is to agree with the participant in the accident on personal compensation for damage without calling government agencies and insurers. This method is quite risky, since not every driver will agree to it if you are at fault. If the accident happened because of another person, such a conditional agreement does not guarantee that he will actually compensate for the damage. This method should be used if the amount of damage is less than the percentage increase in the cost of insurance renewal after increasing the CBM.
It must be taken into account that attempts to avoid increasing the coefficient in the event of one’s own guilt may lead to administrative and criminal liability.
Video on the topic: OSAGO 2021
Catalog of insurance companies in Russia
By following the link , you can familiarize yourself with the catalog of insurance companies in the Russian Federation offering compulsory motor vehicle insurance services. Description of organizations, current financial indicators, ratings, reviews and other information. If you have already had a positive or negative experience with compulsory motor liability insurance of any insurance company, leave your feedback. Thank you!
Link again. Also, be sure to write your comment below. What do you think about the topic of this material? Or maybe you have questions? Ask!
Nuances
Inexperienced car owners should know that by changing their insurance company, their CBM remains at the same level as it was. Many unreliable insurers use a person's ignorance to their advantage by assigning him a third class after issuing a policy. The main argument they provide is the lack of data about the driver in the general database of insurers. There are several solutions to this situation:
- contacting the insurer who served the driver previously;
- obtaining a certificate from the Union of Insurers;
- personal check of the car insurance base.
The insurer does not have the right to independently change the basic rates. If the driver encounters such a situation, he needs to file a complaint with law enforcement agencies. But the OSAGO coefficient can be changed if:
- the driver lied about the circumstances of the traffic accident;
- if the accident occurred due to his intentional fault;
- the car owner was under the influence of alcohol at the time of the accident;
- he fled the scene of the incident;
- The driver had previously driven without insurance.
If the accident was not the fault of the driver, but the KBM for him remains at the same level. However, he should get a 5% discount when renewing his insurance policy for the next year.