The concept of an insured event is the same in most cases. However, there are situations when this concept differs between the car owner and the insurance company. And it often turns out that the damage is caused, the owner of the MTPL policy is sure that the insurance will cover it, but the insurance company finds a thousand reasons not to do this.
The problem is usually that many car owners do not fully understand what the object of insurance under compulsory motor liability insurance is.
Subjects and rates of car insurance
Thanks to the MTPL policy, the motorist has the opportunity to protect his property interests to the victim in the amount of no more than four hundred thousand rubles, in the event that the insured violates traffic rules, resulting in an accident.
The law of the Russian Federation establishes that all car owners must insure their civil liability to third parties. Insurance tariffs are regulated in accordance with the Federal Law, which establishes economically justified maximum tariff levels, as well as their structure and the procedure for implementation by insurance agents when determining the insurance premium.
When calculating tariffs, the share of the insurance premium to pay compensation to the victim must be equal to or exceed eighty percent of the premium amount. The established tariffs are valid for at least six months. Insurance statistics must be officially published annually. It is unacceptable to provide compensation to some categories by increasing the amount of insurance premiums to other categories of persons.
When tariffs increase, the insurance premium remains the same as at the time of signing the contract, according to the previous tariffs. The subjects of compulsory motor insurance are insurers providing insurance services on the basis of a license, intermediaries (various agencies), policyholders (purchasers of an insurance policy), and third parties (victims of road accidents). Compensations are issued through RSA, which is also a subject of OSAGO.
What is OSAGO?
OSAGO car insurance should be carried out by every car owner in order to reduce financial expenses in the event of an accident on the road due to his fault. Today, even very experienced drivers are not insured against such a situation, so the need for a “vehicle license” is regulated at the legislative level. Thanks to the presence of policies on both sides, victims of an accident receive full compensation for damage.
The abbreviation OSAGO has a fairly simple decoding, and it sounds like “Compulsory Auto Civil Liability Insurance.” The active use of the term began in the early 90s, and today the concept is familiar to every person who has bought a car.
Basic principles of “auto citizen”:
- Payments are made by the insurer that issued the policy to the person responsible for the accident.
- Compensation is provided in the form of money transfers, car repairs, tow truck services, payment for rehabilitation and treatment.
- Driving a vehicle without a valid insurance policy is prohibited and will result in penalties.
- The new owner must sign an agreement with the insurer within 10 days after purchasing the vehicle.
- The amount of payments for each specific situation is calculated individually, but cannot exceed 400 thousand rubles.
It is important to know! If, as a result of the accident, no harm was caused to life and health, then a policy such as OSAGO allows you to contact the insurance company directly without involving traffic police officers, which significantly simplifies the procedure for both parties.
Responsibility for absence
Professional liability insurance is insurance of the policyholder's property interests associated with liability for harm caused to third parties as a result of errors or omissions committed in the performance of professional duties.
2 risk groups are insured:
- Risks associated with the possibility of causing bodily injury and harm to health to third parties. Risks associated with the activities of doctors, pharmacists and others.
- Risks associated with the possibility of causing material damage, including loss of the right to make claims. Risks associated with the activities of notaries, architects, auditors, civil engineers and others.
The risks of liability for harm caused intentionally, through deception, or crime are not compensated.
Insurance compensation for this type of insurance does not exceed a certain limit (deductible). The work of independent experts to determine the amount of loss is also deducted from the cost of damage.
The legislation also provides for certain penalties for the absence of a compulsory motor liability insurance policy. At the same time, the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provides for several articles at once.
If the driver has not purchased the document, he may be fined in the amount of 500-800 rubles. Also, the traffic police inspector has every right to detain and send the vehicle to a penalty area. The driver will be able to pick up his car only after presenting the insurance policy.
These are the main measures of liability for the absence of a compulsory motor liability insurance policy.
Insurance options
Auto insurance under the MTPL policy determines compensation only to the injured party in the event of the occurrence of certain risks. The culprit repairs and receives treatment at his own expense. If you want to completely protect yourself on the road, in addition to this type of contract, you can additionally sign up for CASCO insurance. Today, the new MTPL policy provides the following compensation options:
- Harm caused to human life or health.
- Damage sustained to property.
- Compensation as a result of the death of the injured party in an accident (funeral payment).
- Payment for missed work days in case of loss of daily earnings.
- Reimbursement of expenses for sanatorium, medicines, treatment.
The company, when calculating compensation under the policy, takes into account all the factors and circumstances of the incident, as well as the degree of damage received. In case of complete loss of the vehicle, compensation is made based on the value of the car at the time of the insured event; in case of partial damage, only repairs are made.
Business insurance.
- Entrepreneurial risk and its types.
- Commercial risk insurance.
- Technical risk insurance.
- Insurance against losses due to business interruptions.
- Financial risk insurance.
I. Entrepreneurial risk and its types.
Business insurance means “the risk of losses from business activities due to violation of their obligations by the entrepreneur’s counterparties or changes in the conditions of this activity due to circumstances beyond the entrepreneur’s control, including the risk of not receiving expected income” (Article 929 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
1. Disruption of the production process in the event of natural disasters, accidents and other similar events;
2. Changes in market conditions, failure to fulfill contracts on the part of suppliers or consumers of products (services), etc.
The most common types of this insurance are:
- Commercial risk insurance.
- Insurance against loss of profit due to interruptions in production.
- Insurance against the risks of introducing new technology.
- Financial risk insurance.
- Insurance of exchange and currency risks.
II. Commercial risk insurance.
The purpose of this insurance is to compensate the policyholder for possible losses if, after a certain period, the insured operations do not provide the payback stipulated by the contract. They are compensated for losses arising as a result of unfavorable unpredictable changes in market conditions, failure to fulfill contracts or other unforeseen circumstances.
Insurance does not cover losses caused by:
- intermediary activities;
- gambling and speculative transactions;
- decision of the currency authorities;
- changes in currencies;
- political upheavals;
- bank refusal to lend.
- intentional actions of the policyholder, partners or beneficiary to disrupt the insured activity or their violation of the law.
The insured amount for this insurance is established:
- When insuring investments - within the limits of the policyholder's capital investments in the insured operations.
- When insuring income - within the limits of all commercial investments and expected profits.
This insurance is carried out using a minimum deductible of 3-5% and establishing a maximum amount of compensation.
Insurance payment rates depend on the type of activity, insurance period, degree of stability of market relations, and interest rates on loans.
Everything you need to know about vehicle insurance
Everything you need to know about vehicle insurance
A car is subject to various dangers: it can get into an accident, it can be stolen, etc. To protect themselves from losses, companies insure their vehicles. Auto insurance contracts can be of two types: property insurance contract (Article 930 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) and civil liability insurance contract (Article 931 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In the first case, the insurance company compensates for damage caused by damage or theft of the car, and in the second, damage caused by a car that belongs to you, another company or a citizen. In this article we will focus on the features of accounting and taxation of two types of car insurance.
Compulsory motor third party liability insurance
What is OSAGO?
This type of insurance is mandatory when an enterprise is forced to carry it out due to the fact that it is obligated to do so by some law (clause 3 of Article 3 of the Law of the Russian Federation of November 27, 1992 No. 4015–1 “On the organization of insurance business in RF").
Federal Law No. 40-FZ of April 25, 2002 “On compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners” obliges companies with vehicles to insure the risk of their civil liability. Civil liability may arise as a result of causing harm to the life, health or property of others when using vehicles.
Owners of vehicles are those companies that not only own a car, but also use vehicles by proxy or rent them.
There is an exception though. An organization will not have to insure civil liability if it rents a vehicle “with a crew” (the car is maintained by its owner). In this case, all costs of insuring both the vehicle itself and liability for damage caused by it are borne by the lessor.
If a company uses the car of its employee under a bareboat rental agreement or under a gratuitous use agreement, then the owner of the vehicle, and therefore the insured, is the organization.
If an organization pays compensation to an employee for using a personal car for business purposes, then the employee himself must insure his civil liability. Rules of "motor citizen"
It is necessary to insure civil liability no later than five days after the organization receives the right to own a vehicle (Clause 2, Article 4 of Law No. 40-FZ). Otherwise, the car will not be allowed for technical inspection and will not be registered with the traffic police.
The rules for compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners were approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 7, 2003 No. 263.
In order to insure civil liability, you need to enter into an agreement with an insurance company that has the appropriate license. To do this, the organization must submit the following documents or copies thereof to the insurance company:
- application for concluding a compulsory insurance agreement in the form given in Appendix No. 1 to the Insurance Rules;
- certificate of registration of a legal entity;
- passport or registration certificate of the vehicle specified in the application for concluding an insurance contract;
- driver's licenses of persons who are allowed to drive a car, as well as documents confirming the driver's right to drive this vehicle.
A vehicle may have several owners - owner, lessee, etc.
One of them has the right to insure the liability of all the others. To do this, they need to be listed in the contract with the insurance company. After the contract is signed, the insurance company must present the owner of the vehicle with an insurance policy in the form given in Appendix No. 2 to the Insurance Rules, as well as a special state-issued sign. This sign must be placed on the vehicle in the lower right corner of the windshield.
In the event that an insurance policy or a special sign is lost, the insurance company is obliged to issue a duplicate of these documents. This is done for a fee, the amount of which is determined by the cost of making duplicates.
The insurance company must also issue two accident notification forms to the organization.
It must be filled out in the event of an accident and handed over to the insurer within 5 days from the date of the accident. The civil liability insurance contract is concluded for a period of at least one year (Article 10 of Law No. 40-FZ). Then its validity will be extended until the policyholder notifies the insurance company of the termination of the contract. Moreover, he must do this no later than two months before the contract expires. On the other hand, the contract may be terminated if the vehicle owner is more than 30 days late in paying insurance premiums for the next year.
Insurance premium
Vehicle owners who have insured their civil liability must pay premiums to the insurance company. This is the so-called insurance premium, which is paid in one-time or partial payments. Its size is calculated based on insurance rates, which are established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 8, 2005 No. 739.
Insurance rates will be the base rate and odds. The insurance premium is equal to their product. The amount of insurance depends on the category of the owner of the car (individual, legal entity or taxi owner). The basic tariffs for them are 1,980 rubles, 2,375 rubles. and 2,965 rub. respectively.
In addition, the size of the tariff also depends on the age and experience of the driver, and the place of registration of the car. For example, in Moscow this coefficient is 2.
The make of the car and its age are not taken into account, but the term of the contract and the period of use of the car are taken into account.
The amount of insurance premium for cars, taxis (including minibuses) is today calculated using the following formula:
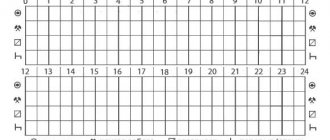
SP = TB x KT x KBM x KVS x KO x KM x KS x KP x KN,where TB is the base insurance rate in rubles (see Table 1).
Insurance rates coefficients depending on:
CT - from the territory of primary use of the vehicle;
KBM - on the presence or absence of insurance payments in the event of insured events that occurred through the fault of the policyholder during the period of validity of previous compulsory insurance contracts. If the insurance contract is concluded for the first time, then the BMR is taken equal to 1;
PIC - from the owner of the car (individual/legal entity), age and length of service of the driver;
KO - on the number of persons allowed to drive a vehicle;
KM - from the engine power of a passenger car (see Table 2);
KS - from the period of use of the vehicle; CP - from the insurance period (see Table 3);
KN - from the good faith of the policyholder. Its value depends on how reliably the person provided the information necessary to conclude a contract, or information about the circumstances of the case in an accident.
Table 1
Table 2
Coefficients applied depending on engine power
Table 3
Insurance rate coefficients depending on the insurance period
If the insurance company convicts the organization of providing it with false information, which resulted in the payment of an insurance premium in a smaller amount, then it will apply a CI coefficient of 1.5.
The same coefficient will be applied if the accident was committed intentionally or the circumstances of the accident were deliberately distorted in order to increase the insurance payment.
Finally, the insurance company can also apply the specified size of the KN coefficient when harm is caused under circumstances that were the basis for filing a regressive claim.
Example 1
The car belongs to Stalker LLC. The base rate of the insurance tariff (TB) for it is 2,375 rubles. The car was purchased and registered in 2006.
The territory of primary use is Moscow (CT = 2).
The contract of compulsory motor third party liability insurance is concluded for the first time (KBM = 1).
The age of the drivers indicated in the insurance policy is 27 years old, driving experience is 1.5 years (DIC = 1.15).
Two drivers specified in the compulsory insurance contract are allowed to drive the car (CO = 1).
Engine power is 119 hp. With. (KM = 1.3).
The period of use of the car is 12 months a year (KS = 1).
The insured is recognized as being in good faith, therefore the KN coefficient is not applied.
SP = 2,375 rub. ? 2? 1 ? 1.15? 1 ? 1.3? 1 = 7,101.25 rub. (in year).
Note! The amount of the insurance premium cannot exceed three times the base rate of insurance tariffs, adjusted by the regional coefficient. In the example given, the maximum amount of the insurance premium should not exceed RUB 14,250. (RUB 2,375 ? 2 ? 3).
In tax accounting, expenses for compulsory types of insurance are included in other expenses within the limits of insurance tariffs, which are approved in accordance with Russian legislation.
This is established by paragraph 2 of Article 263 of the Tax Code. Thus, as part of other expenses, an enterprise can include the amount of insurance calculated for it at the established rate.
If the tariffs are not approved, then the costs of compulsory insurance are included in other expenses in the amount in which they were actually paid.
Please note: in some cases, tax authorities take the exact opposite position. Article 263 of the Tax Code does not directly indicate that it applies not only to the costs of property insurance, but also to the costs of compulsory civil liability insurance for vehicle owners. This gives tax authorities reason to believe that vehicle insurance costs do not reduce taxable profit. They believe that an organization can reduce its taxable profit only by the amount of expenses for compulsory types of property insurance.
New information about insurance coefficients
At the end of last year (November 8, 2006), the State Duma of the Russian Federation adopted in the third reading amendments to the law “On compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners,” which establish the procedure for applying the coefficient depending on the presence or absence of insurance payments (“ bonus-malus"). The new law will come into force 90 days after its publication.
The current version of the “Law on Compulsory Civil Liability Insurance of Vehicle Owners” (No. 40-FZ) provides the following description of the KBM coefficient:
"2. The coefficients included in the insurance tariffs are set depending on: ... the presence or absence of insurance payments made by insurers when carrying out compulsory civil liability insurance of the owners of the specified vehicle in previous periods.”
The version of the bill adopted in the second reading proposes the following option:
"2. The coefficients included in the insurance tariffs are set depending on: ... the presence or absence of insurance payments made by insurers in previous periods when implementing compulsory insurance of civil liability of the owners of this vehicle, and in the case of compulsory insurance for limited use of the vehicle, which involves driving means only by the drivers specified by the policyholder - the presence or absence of insurance payments made by insurers in previous periods when implementing compulsory civil liability insurance for each of these drivers.”
According to the deputies, this innovation will help eliminate injustices in the application of the bonus-malus coefficient, namely when the accumulated bonus was lost when the policyholder, an individual, changed the vehicle.
In fact, now accident records must be kept for each driver separately, that is, all accidents that a driver commits in any car will increase the cost of compulsory motor insurance for him. For example, a driver violated traffic rules at work (driving a Kamaz) and got into an accident - now even when insuring his personal car, he will pay an increasing bonus-malus coefficient.
Moreover, the tariff will be increased for all cars where our “emergency” driver is listed as a person allowed to drive. Today, the average Russian driver is allowed to drive three cars. Consequently, on average, an insurance company, having made one payment under MTPL, will have the opportunity to increase the rate under three contracts at once.
If this bill is adopted, the meaning of the Insurance Certificates, which insurers must issue to policyholders upon termination of a contract, will be lost. After all, a driver can be simultaneously insured by several insurance companies (included in the policies of different cars). Therefore, to prove your positive insurance history, you need to bring certificates from all insurance companies! This problem can be solved with the help of a single computer database, but will insurers be able to implement this database within 90 days after the adoption of the law, and most importantly, ensure access to it for all selling divisions and agents throughout the country?
Information about the policyholder history of each driver will now be needed not only when moving from one insurance company to another, but also when renewing a contract in the same insurance company, making changes to the contract, or adding a new driver to the policy. All this will significantly complicate these procedures and, accordingly, increase the time required for processing documents. For example, if today almost every agent can add a new driver to the policy, then after changes in the law this can only be done after receiving a request from the database - most likely, the time frame for making changes to MTPL policies will increase to 2 days.
Procedure for receiving insurance compensation
To receive insurance compensation under compulsory motor liability insurance, an organization must notify insurers of the occurrence of an insured event within five working days after an accident. To do this, you need to submit to the insurance company:
- an application for insurance compensation in any form;
- notification of an accident (the form of this document was approved by order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation dated June 14, 2003 No. 414);
- certificate of participation in an accident (Appendix No. 12 to the Methodological Recommendations for organizing the activities of traffic police units in proceedings on cases of administrative offenses (letter of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation dated June 18, 2003 No. 13/ts-72));
- a copy of the protocol on the administrative offense (Appendix No. 1 or No. 2 to the Methodological Recommendations).
After the injured party receives the remaining documents, they are also transferred to the insurance company. This is about:
- certificate of participants in the accident (Appendix No. 31 to the Methodological Recommendations);
- copies of the resolution in the case of an administrative offense in the event of an administrative offense;
- documents confirming the organization’s ownership of damaged property or the right to insurance payment in case of damage to property owned by another person;
- the conclusion of an independent examination on the amount of damage caused;
- documents confirming payment for the services of an independent expert, if payment was made by the victim;
- documents confirming the provision and payment of services for the evacuation of a damaged vehicle from the scene of an accident to the place of its repair or storage;
- documents confirming the provision and payment for services for storing damaged property from the day of the accident until the day the insurer conducts an inspection or independent examination.
If property was damaged during an accident, then its remains must be submitted to the insurance company.
She, in turn, must conduct an inspection and independent examination of the damaged property. To do this, she is given 5 working days from the date of receipt of the application for insurance payment from the victim. If the vehicle is severely damaged as a result of an accident and it is impossible to deliver it to the insurance company, then the inspection and assessment of such property within the same time frame is carried out at its location.
Please note that insurance compensation will be paid to the organization only after providing a complete package of documents.
Within 15 days from the date of receipt of documents confirming the insured event, the insurance company must compensate the losses to the injured party or send a reasoned refusal to pay insurance compensation.
Amount of insurance compensation
If damage is caused to life and health, then the victim must be compensated for the lost earnings (income) that he had or could have had on the day the harm was caused to him. In addition, the insurance company must compensate for additional expenses incurred:
- for treatment;
- additional food;
- purchasing medicines;
- prosthetics;
- outside care;
- Spa treatment;
- acquisition of special vehicles;
- preparation for another profession.
As part of the insurance payments, damage caused as a result of the loss of a breadwinner, as well as funeral expenses, are also compensated.
If damage is caused to property, the insurance company must compensate the victim for its real value, which is determined depending on the condition of the property. In case of complete loss of property, expenses can be reimbursed in the amount of its actual value on the day of the accident. This also applies to those cases when the cost of restorative repairs of a vehicle involved in an accident is equal to or greater than its value before the accident.
If the car is not completely damaged, then the damage is compensated in the amount of restoration costs, that is, those costs that are necessary to bring the property to the condition in which it was before the insured event. These include:
- materials and spare parts necessary for repair work;
- expenses for vehicle repair work.
If, as a result of an accident, not only the vehicle, but also real estate located at the site of the accident is damaged, then the organization’s expenses for the delivery of material and spare parts to the place of repair of this property, as well as the costs of delivering repair crews to the place of repair and back, are also subject to compensation. .
The insurance organization determines the amount of expenses taking into account the wear and tear of parts, assemblies, assemblies and parts used during restoration work. Vehicle repair costs are paid based on the average prices prevailing in the relevant region.
In addition, the insurance company will reimburse the organization for the costs of evacuating the vehicle from the scene of the accident to the place of repair or storage, as well as the costs of storing it from the day of the accident until the day of inspection by the insurer or until the day of an independent examination.
The maximum insured amount under compulsory motor liability insurance, within which the insurer will compensate the insured for the damage caused, is 400,000 rubles. (Article 7 of the Law on Compulsory Insurance). From this amount to compensate for damage caused:
- life or health, if there are several victims, 240,000 rubles, one victim - no more than 160,000 rubles;
- property, if there are several victims - 160,000 rubles, one victim - no more than 120,000 rubles.
The specified insurance amounts are paid in each insured event. This means that if a car is involved in several accidents within a few hours, then for each of them the maximum insured amount will be 400,000 rubles.
If a criminal or civil case is opened as a result of an accident, the amount of payment may depend on the results of the proceedings in these cases. The period of insurance payment in this case is extended until the end of this proceeding and the entry into force of the court decision. The same mechanism applies when initiating a case of administrative violations. At the request of the policyholder, the insurer must issue a calculation on the basis of which the amount of the insurance premium was determined.
Voluntary car insurance
Features of voluntary car insurance
Insurance, which the company carries out at its own discretion, is voluntary. The company can insure the car against theft or damage. To do this, you need to conclude a property insurance agreement with an insurance company. The contract must indicate the following main points:
1. Duration of the contract (usually one year).
2. The amount of insurance premiums and the procedure for their payment.
3. Insured events (situations in which the insurance company pays compensation).
4. Sum insured (the maximum amount that can be paid in an insured event). It should not be more than the value of the insured vehicle.
The insurance contract begins to be valid on the day the organization pays the first installment (Clause 1, Article 957 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the company is issued an insurance policy. It will need to be presented to the insurer in the event that something happens to the car.
The company can also insure a rented vehicle if its owner has not done so. After all, it is the tenant who will have to reimburse expenses in the event of damage (Article 669 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Accounting and taxation
Expenses for voluntary insurance of vehicles that are used to generate income are also taken into account when calculating the tax base for income tax (subclause 1, clause 1, article 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, this fully applies to rented cars.
The terms of the insurance contract may provide for payment of the insurance premium in a one-time payment. Then, for contracts that are concluded for more than one tax period, expenses are recognized evenly over the term of the contract.
In accounting, vehicle insurance costs are expenses for ordinary activities (clause 5 of PBU 10/99). Insurance costs must be reflected in the accounting period to which they relate, regardless of the time of their actual payment. The enterprise reflects a one-time payment for the year on account 97 “Deferred expenses”, and then monthly writes off 1/12 of its part to the accounts of production and sales costs.
The amount of insurance compensation received by an organization upon the occurrence of an insured event is not subject to VAT.
Taxable profit can be reduced by the amount of insurance premiums (Article 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It does not matter which vehicle the organization insured - its own or a rented one. The main thing is that it is used in production activities. A prerequisite for recognizing such expenses is the actual payment of the insurance premium.
The procedure for tax accounting of insurance premiums depends on the method by which the organization accounts for income and expenses. If the accrual method is used, then in tax accounting, as well as in accounting, insurance premiums must be included in expenses in the reporting period to which they relate. This means that when paying an insurance premium in a one-time payment, insurance costs are included in other expenses evenly throughout the entire term of the contract.
Tax accounting of vehicle insurance costs can be maintained using accounting data.
Example 2
On November 1, 2006, Zigzag LLC entered into an agreement to insure a passenger car against theft for a period of one year with a one-time payment of an insurance premium in the amount of 18,000 rubles. The organization determines income and expenses using the accrual method. The monthly amount, which is included in expenses, both in tax and accounting, will beRUB 18,000: 12 months. = 1,500 rub.
The following entries were made in the accounting records of Zigzag LLC:
Debit 97 Credit 76 subaccount “Calculation for property insurance” - 18,000 rubles. — the enterprise’s debt under the insurance contract is reflected;
Debit 76 subaccount “Calculation for property insurance” Credit 51 - 18,000 rubles. — reflects the enterprise’s debt under the property insurance contract.
Monthly:
Debit 26 Credit 97 - 1,500 rub. — part of the costs of car insurance is included in general business expenses.
In tax accounting for 2006, the amount of insurance payments in the amount of 3,000 rubles must be included in other expenses. (RUB 1,500 = 2 months). And in 2007, the amount of 15,000 rubles will be included in other expenses. (18,000 rubles - 3,000 rubles).
Organizations that use the cash method to determine income and expenses can reduce their taxable profit by the entire amount of insurance expenses in the month when the premium was paid (clause 3 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, tax accounting data will not coincide with accounting data. Compulsory motor third party liability insurance allows you to transfer compensation for damage caused to third parties to the insurance company. This means that if the organization’s vehicle causes harm to the life, health or property of the victim, then the insurance company will compensate for the damage caused.
Please note that the insurance company will not compensate for damage that was caused as a result of force majeure or as a result of the intent of the victim.
Thus, insurance compensation is the amount that is paid in the event that the vehicle is damaged due to extraordinary circumstances. The fact that extraordinary events actually occurred must be documented.
Accounting and tax accounting of insurance payments
The expenses incurred by the organization in an insured event are extraordinary expenses (clause 13 of PBU 10/99). Therefore, they need to be taken into account in account 99 of the “Extraordinary Expenses” subaccount. Insurance compensation paid to an organization is considered extraordinary income. It must be taken into account in account 99 of the “Extraordinary Income” subaccount. The amount of compensation depends on the damage caused to the vehicle.
In tax accounting, compensation is included in non-operating income that increases taxable profit (Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And the expenses incurred by the enterprise due to an insured event are included in non-operating expenses (subclause 6, paragraph 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Example 3
In September 2006, Grom LLC insured its car in case of an accident in the amount of 290,000 rubles. In December of the same year, the car was badly damaged in an accident. The car cannot be repaired or restored. This is confirmed by an accident report issued by the traffic police, as well as a certificate received from an independent appraiser. The company decided to write off the car. An insurance claim was received from the insurance company.
The initial cost of the car in accounting and tax accounting is 400,000 rubles. The amount of depreciation accrued at the time of the accident, both in accounting and tax accounting, is 100,000 rubles. Grom LLC paid 2,000 rubles for conducting an independent examination.
In tax accounting, Grom LLC uses the accrual method to determine income and expenses.
The following entries were made in accounting:
Debit 76 subaccount “Calculations for property and personal insurance” Credit 99 subaccount “Extraordinary income” - 290,000 rubles. — insurance compensation has been accrued;
Debit 51 Credit 76 subaccount “Calculations for property and personal insurance” - 290,000 rubles. — insurance compensation has been transferred;
Debit 01 subaccount “Retirement of fixed assets” Credit 01 subaccount “Fixed assets in operation” - 400,000 rubles. — the original cost of the car has been written off;
Debit 02 Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - 100,000 rubles. — the amount of depreciation accrued at the time of the accident is written off;
Debit 99 subaccount “Extraordinary expenses” Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - 300,000 rubles. (400,000 rubles - 100,000 rubles) - the residual value of the car is written off;
Debit 99 subaccount “Extraordinary expenses” Credit 76 subaccount “Settlements with other creditors” - 2,000 rubles. — the cost of an independent examination is taken into account;
Debit 76 subaccount “Settlements with other creditors” Credit 51 - 2,000 rubles. — paid expert services.
In tax accounting, insurance compensation (290,000 rubles) is included in non-operating income. And the residual value of the car and the cost of the examination (300,000 rubles + 2,000 rubles) are included in non-operating expenses. Consequently, in December 2002, the taxable profit of Grom LLC will be reduced by 12,000 rubles.
When rental property is insured, the accounting for compensation depends on who the contract is in favor of.
After all, an insurance contract can be concluded both in favor of the tenant and in favor of the lessor (Article 930 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). If insurance is paid to the landlord, it is not reflected in the tenant's accounting. If the insurance compensation is received by the tenant, then the accounting and tax accounting of this operation is exactly the same as in the case when one’s own property was damaged.
F.N. Filina, economist-analyst
Reinsurance Basics
- The essence and main functions of reinsurance.
- Facultative and obligatory reinsurance.
- Proportional and non-proportional reinsurance.
Reinsurance is insurance by one insurer (reinsurer) under the conditions specified in the contract for the risk of fulfillment of all or part of its obligations to the insured by another insurer (reinsurer).
The risk transferred is called reinsurance risk. The process associated with the transfer of risk - risk assignment or reinsurance cession.
The reinsurer is called the cedant, and the reinsurer is called the assignee.
The risk accepted by the reinsurer from the reinsurer may be subject to subsequent transfer in whole or in part to another reinsurer. The subsequent transfer of the reinsured risk is called retrocession. An insurance company that transfers the risk to reinsurance to a third party is called a retrocedent, and one that accepts the risk is called a retrocessionary.
1. Ensuring the financial stability of the insurer.
It is achieved by fragmenting the risk and distributing it among a large number of insurance companies.
When transferring risk to reinsurance, it is important to determine the amount within which the insurance company retains its share of the insured risks - the company’s own retention.
If the deductible limit is underestimated, the insurance company will lose part of its income, because will transfer the excess portion of the insurance premium to reinsurance.
If the limit is too high, this may adversely affect the results of one’s own financial activities.
2. Protection of property interests of policyholders.
Ensures that the insurer fulfills its payment obligations to the policyholder.
H ≤ A – O, where
A – the size of the insurer’s assets;
O – the volume of the insurer’s obligations (amount of insurance reserves).
N – the minimum permissible amount of excess of the insurer's assets over its liabilities.
N = 5% of the insurance reserve.
N = 16% of the amount of insurance premiums received for the year.
Thus, the essence of reinsurance lies in “secondary” insurance of insurers against risks exceeding the solvency of the insurance company.
By transferring risks to reinsurance, the reinsurer receives the right to a bonus, i.e. commission on the profit that the reinsurer can receive when implementing the contract.
In practice there are:
- Active reinsurance.
It involves transferring risk.
- Passive reinsurance.
It is about taking risks.
Active and passive reinsurance can be carried out simultaneously by the same insurance company. In this case it will act as:
- insurer;
- reinsurer;
- reinsurer.
In accordance with current legislation, vehicles are sources of increased danger. Accordingly, their owners must compensate for the damage caused to third parties.
To purchase an MTPL policy, you must enter into an appropriate agreement with the insurance company. It is the agreement concluded between the vehicle owner and the insurance company that is the basis for covering losses caused to third parties.
Of course, only those companies that have the appropriate permit (license) can act as insurers. You also need to know that the law establishes the main points that must be included in the insurance contract.
The object of insurance is the property interests of the owner of the vehicle, which are associated with his obligation to compensate for losses caused to third parties.
Features and driver rights
The very definition of compulsory motor liability insurance contains the essence of the contract that is concluded with the company. It is motor third party liability that is insured. The signed agreement gives the driver his rights (receiving compensation in the event of an accident through no fault of his own), but also imposes responsibilities. In particular, these include:
- Immediately contact the official representative of the company in the region in writing if the risks described in the policy occur.
- Exchange of data on the insurance contract with the other party to the accident and registration of the Euro Protocol, if, by agreement of the parties, a decision is made not to involve traffic police officers.
- At the request of company employees, the policyholder must provide in full all data about the incident, video or photographic recording of the damage caused to the vehicle.
- In case of an accident, the driver is obliged to take all necessary measures to reduce damage, reasonable and available in a particular situation, regardless of who was at fault.
In addition, the owner of the transport
means is free to choose an insurer at his own discretion and enter into an agreement with him for the provision of services. At the same time, experts always recommend paying attention to the reliability of the company, getting acquainted with the ratings on the market in order to use the offers of only those operators who strictly fulfill their obligations in the event of an accident. In addition, the driver has the right, in case of loss of the policy, to issue a duplicate, terminate the contract unilaterally, and also receive full compensation if damage is caused to the vehicle on the road due to the fault of the other party.
The procedure for making insurance compensation and monitoring its compliance
From the first of July 2014, the payment limit for compulsory motor liability insurance concluded after October 1, 2014 is four hundred thousand rubles in case of compensation for damage to a car. Previously, the maximum payment amount was one hundred twenty thousand rubles. It is also planned in 2015, no earlier than April, to increase the amount of payments for compensation for health and life.
To receive compensation, the victim can contact not only the insurer of the person responsible for the accident, but also directly to his insurance company if all participants in the accident have a compulsory motor liability insurance policy.
Types of compulsory motor liability insurance
Compulsory car insurance can be divided into the following types:
- limited. The car owner for whom the MTPL policy is issued is obliged to include in the document information about the people allowed to drive his vehicle. Their number should not be more than five people. The form contains not only the personal data of the drivers, but also their license numbers. This condition is provided so that the insurance company can check the driving history of each individual and set the price for the policy. In other words, if one of the trusted persons has been involved in one or more accidents in the past, then the cost of mandatory auto insurance may increase significantly;
- unlimited. This type of compulsory motor liability insurance costs slightly more than a limited policy, since it does not provide for a list of authorized persons to drive a specific vehicle. Consequently, the car can be driven by anyone with a driver's license, which means that the likelihood of accidents on the road increases. It is for this reason that insurers increase the cost of unlimited compulsory motor liability insurance;
- paper The classic type of OSAGO policy is a form printed on paper, which is issued to the driver by representatives of the insurance company. It records all information about the car and other details of the interaction between the driver and traffic police officers. You can always take your paper OSAGO policy with you and present it to the traffic inspector if necessary. However, it is worth noting that recently cases of forgery of compulsory car insurance forms have become more frequent;
- electronic. Thanks to modern technologies, you can issue an MTPL policy without leaving your home. To do this, you just need to have an Internet connection. A car owner who applies for an electronic form of OSAGO will not receive a paper form as with standard registration, but will still be included in the database of the Russian Union of Auto Insurers (RUA). If you only have an electronic policy, interaction with the traffic police becomes a little more complicated, because the driver himself must provide the police with basic information about his insurance for a successful search in the database. If the owner of the vehicle gives incorrect information about his MTPL, the traffic inspector will not be able to find the policy in the RSA database and will impose a fine for lack of compulsory insurance. To avoid ending up in a similar situation, experts recommend that drivers take with them a printout of the electronic OSAGO policy;
- tourist. If a car owner decides to drive his car outside of Russia, then he should know that the classic OSAGO policy is not valid abroad. Therefore, in order to avoid fines and other misunderstandings as a result of lack of insurance, the car owner must purchase a tourist type of compulsory insurance. The policy will be valid for 20 days;
- seasonal. This type of MTPL is suitable for those car owners who use their vehicle only for a certain period of time. It is for this reason that its cost is lower than a regular policy.
In addition to the above, compulsory motor third party liability insurance also differs in its validity period (from 3 to 12 months).
If you purchased another policy
Compulsory motor liability insurance is mandatory and, based on the law, the driver is required to purchase a compulsory insurance policy. Since CASCO is voluntary, the question of purchasing it is at the discretion of the driver.
CASCO is a more expensive insurance, and has more possibilities for insurance cases, but CASCO is voluntary insurance and is taken out at the discretion of the driver.
Insurance of property of citizens is very diverse and can concern relatively independent types of insurance. The objects of property insurance are:
- means of transport (personal transport). The most common type of property insurance for citizens is insurance of vehicles - against theft, damage, intentional actions of third parties, etc.;
- residential premises (including apartments and individual rooms within the city) and their component structures (various types of floors, dividing partitions, etc.), as well as finishing elements that can be repaired and improved (wall, ceiling, floor coverings) , individual elements and equipment of heating (autonomous) and sewerage (toilets, sinks, baths), - insurance against damage, destruction: due to flooding with water, as well as the actions of third parties;
- three buildings (residential houses, cottages, cottages, outbuildings, bathhouses) and their component structures (roofing, floors, foundations) - insurance of household property: against fire, landslides, groundwater, earthquakes, soil subsidence, water penetration from rainfall, hail, etc.;
- other household property (household items, documents and securities, precious and semi-precious metals and a fireplace) - insurance against fire (fire insurance), water penetration, theft, damage, etc. It should be said that such insurance objects can be insured for special conditions - in the form of an addition to the main agreement;
- pets – animal life insurance, theft, loss, etc.
Among the many types of property insurance for citizens, the following property insurance objects are distinguished:
- the object is a variety of material values;
- personal insurance, where the objects of insurance are events in the lives of individuals;
- liability insurance, the subject of which is compensation for the insured's obligation to compensate for damage (harm) to third parties.
As mentioned above, property insurance can be:
- voluntary, the procedure is determined on the basis of the agreement of the parties (the policyholder and the insurance organization) regarding the terms of insurance;
- mandatory when such insurance is required by law.
Special types of property insurance are reinsurance and coinsurance. These types of insurance allow you to distribute and redistribute large risks between different insurance companies.
In addition to the common types of property insurance, there are others, namely:
- insurance against non-receipt of expected income from various transactions and turnover;
- insurance of banking risks from the purchase of currency, issuance (non-repayment) of loans, etc.;
- commercial risk insurance (may include the two previous types of property insurance);
- insurance of construction risks (simple construction against shortages of building materials, facing materials by partners of the construction company).
In any type of property insurance, the insurance contract stipulates the amount and procedure for payment of insurance compensation; all this must be reflected in the property insurance policy.
Insurance is a necessary necessity. Now you know what applies to property insurance, and “in which direction” you need to move in order, if not to protect yourself completely, then at least to minimize material losses from unforeseen events that can happen to any of us.
Types of policies
OSAGO auto insurance allows you to issue a policy with certain capabilities. Each type has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, which it is better to learn about before signing the contract.
- Insurance with limitations. It is issued for a strictly defined number of people who are allowed to drive a car. It is usually offered to buy for drivers with extensive experience, since in this case the cost of the policy will be more profitable for the client. But driving a vehicle by persons not included in the document is fraught with a fine.
- Insurance without limits. This option is suitable for people who have just received their license, or if the car is used by a large number of people (at least 5). The policy allows anyone to drive a vehicle without the risk of administrative punishment when documents are checked by traffic police officers.
Insurers such as RESO-Garantiya, Renaissance-Insurance and other companies offer a document for one year. Some car owners used to take out a policy for the summer if they used transport seasonally, but since 2021 they no longer have this option. Now the minimum period is a period of 365 days.
What is the difference between voluntary and compulsory property insurance?
Voluntary property insurance is nothing more than the need of individuals and legal entities to protect their property interests, if they (needs) do not run counter to the law and are confirmed by the client’s finances (his ability to pay for certain types of insurance) and his desire to pay ( precisely a desire, not an obligation).
Voluntary insurance is a kind of commodity-money relationship, which in principle it is. Everything is fair here, because no one forces you into this relationship - the demand of the buyer (the policyholder) and the offer of the seller (insurance organization), only the terms of insurance are negotiated. Everything is very clear - if they do not suit you (some conditions), you simply look for another insurer. No one owes nothing to nobody.
Compulsory insurance of property of individuals and legal entities is based on legislation that does not take into account the financial condition of those individuals who may suffer or suffer losses from insurance events that may occur as a result of the actions (inaction) of civil and legal entities.
At the same time, the state cannot fail to take into account the solvency of civil and legal entities when developing laws on compulsory insurance, so that later problems do not arise in matters of the size of insurance premiums and tariffs. Financing of compulsory property insurance comes from two sources:
- own funds and funds of interested parties - sponsors, shareholders, shareholders, etc. Such insurance is subject to the property of enterprises invested by foreigners, temporarily exported cultural property, geological installations and structures, property pledged in a pawnshop, etc.;
- funds from the relevant budgets - property of enterprises, property of individuals (from a man-made disaster or natural disaster, accidents), property of judges, contract military personnel, tax police, etc.
Price formation
It is the responsibility of every driver to carry an MTPL policy. You can purchase it at any branch of your chosen insurer. But buyers often note that the cost of a document may vary slightly in different places. This is explained by the fact that tariff limits are set by firms independently. You can find out how much you will have to pay before contacting the insurance company. A special calculator program presented to users on the website of any company will help with this. It takes into account the following points:
- Type of vehicle (car or truck, motorcycle, scooter).
- The number of drivers who will operate the equipment.
- Age and driving experience on the road.
- Power of the propulsion system.
- For what period is the contract planned to be executed?
- Information about previously issued policies.
It is important to know! The cost of the policy for an individual and a legal entity will differ, so this factor should also be taken into account when making preliminary calculations.
MTPL reform 2014
Summing up, I would like to note that after the reforms of 2014, the MTPL policy became more expensive, but at the same time the amount of payments on it was increased. Also, the government decree changed the procedure for registering road accidents using video recorders to receive compensation, which applies to some regions of Russia for those who issued compulsory motor liability insurance after October 1, 2014.
According to the new Amendments, the requirements for policyholders have been tightened. The period for payment of compensation from September should not exceed twenty days, otherwise the company will be forced to pay a penalty. A penalty has been introduced for failure to indicate the reasons for refusal to pay compensation.
Types and advantages of civil liability insurance
Civil liability implies compensation for damage caused to third parties. For example, if you break your neighbor's glass, you must pay for it. But the blame can be shifted onto the shoulders of the insurance company. There is such a service as civil liability insurance (CLI), where a variety of risks can be specified in the contract.
what satisfied customers say / all reviews
Georgiy
Many thanks to manager Arvid for being able to quickly sort out the problem with the OSAGO coefficient. Literally fought with the insurance company for me. Good luck to you guys!
Alexander
Thank you for such fast delivery of the policy. We have a legal entity, but they don’t yet make electronic MTPL for legal entities, but the guys brought the policy in just an hour.
Paul
Thank you for your detailed advice during the accident. I called Element and they instructed me in detail about my actions in the event of an accident. I wanted to thank them, and they said that the best consultation is a good review on the website. Everyone would work like that.
Arsen
Dmitry helped us deal with the problem. I got into an accident, it was my fault, 2 months later I received a letter from my insurance company that I owe them compensation for the costs of repairing the car I drove into. It turns out that I had to notify them about the accident, since we used the Europrotocol. They actually have such a rule. But Dima helped me avoid this!
Anton
Professionals in their field. Even the courier knows a lot about insurance. He told me a lot of nuances about how to behave in an accident. Thank you!
Natalia
I would like to convey a big thank you to your manager; unfortunately, I don’t remember his name. He filled out the policy very quickly and answered in detail the thousand questions I threw at him.
Catherine
Great service from the guys. It is very convenient that there are all payment methods. Transferred money via PayPal
Evgeniy Mikhailovich
I signed up for compulsory motor liability insurance directly on the website. Didn't talk to anyone. I quickly entered all the information and received a calculation, and the data for my car was found automatically, and I only entered my car number. “What progress has come!”
Types of insurance
In general, SGS can be divided into 2 groups: mandatory and voluntary. In the first case, policies are issued compulsorily. In the second, insurance is issued at the will and desire of the policyholder.
why choose elemins.ru
Better conditions
We will select the best price, make the biggest discount and the best conditions in the best insurance companies
VIP support for each client
We provide maximum support to our clients on all matters related to insurance
100% payment guarantee
We will help you get the payment you are entitled to if a difficult situation arises, since we have excellent connections with all partners
The difference between compulsory car insurance and CASCO
In order to make a comparison between MTPL and CASCO, it is necessary to understand what the latter type of insurance is. CASCO is voluntary insurance of your vehicle against possible accidents on the road and while parked. Each insurance company that provides such a service can establish its own rules and stipulate in the CASCO agreement the rights and obligations it needs.
Consequently, every car owner has the right to choose an insurance company based on the conditions offered. As for the price of a CASCO policy, it is regulated exclusively by insurers and depends on the value of the car and on the assessment of the likelihood of a possible risk occurring. So, the obvious differences between compulsory car insurance and CASCO can be summarized in the following list:
- MTPL policy: covers the civil liability of the insured;
- must be concluded by every car owner;
- all insurers contain the same conditions and rules, which are regulated exclusively by the Government;
- has a fixed cost according to the tariffs of the Ministry of Finance;
- applies only to those traffic accidents for which the person specified in the contract is at fault;
- covers the estimated average cost of repair work according to calculations, taking into account the degree of wear of parts;
- determines 120 thousand rubles for damage to property and 160 thousand rubles for harm to life and health (these amounts are established by the legislation of the Russian Federation);
- has no restrictions on the age of the car;
- applies exclusively to the policyholder’s car;
| CASCO | OSAGO |
| The policyholder's car is insured under CASCO | Compulsory motor liability insurance insures the policyholder's civil liability for harm that he may cause to others when using his car. |
| CASCO – voluntary insurance. | OSAGO – compulsory insurance. |
| The terms of the contract and the CASCO Rules differ in each insurance company - you can choose the most suitable one. | The terms of the contract and the MTPL Rules are the same in all insurance companies - they are established by the Government. |
| The price of a CASCO policy primarily depends on the value of the car, as well as on the assessment of the degree of risk - it differs in different insurance companies. | The price of the MTPL policy is the same in all companies and is determined according to the tariffs established by the Ministry of Finance. |
| Insured events: any accident; illegal actions of third parties (including theft, theft), fire, natural disasters, foreign objects falling on the car, etc. | Insured events: only road accidents in which the person specified in the MTPL policy is at fault. |
| Amount of compensation: The actual cost of repairing the car or its full cost at the time of the insured event is paid. | Amount of compensation: The estimated average cost of repairing the vehicle according to calculations is paid, taking into account the degree of wear of the parts being replaced. |
| Sum insured: under CASCO insurance, the sum insured is equal to the actual value of the insured car at the time of conclusion of the contract. | The insurance amount under compulsory motor liability insurance is determined by law. 120,000 rub. for damage to property, 160,000 rubles. for harm to life and health. |
| In CASCO, the age limit for the insured car is usually no more than 7-10 years. | In OSAGO there are no restrictions on the age of the car. |