Traffic rules of the Russian Federation 2021
STSI EXAMINATION TICKETS for categories “A”, “B”, “M” and subcategories “A1”, “B1”
on the topic Procedure for providing first aid to persons injured in an accident
TICKET 2. Question 20
| In what cases should cardiopulmonary resuscitation of the victim be started? Ticket 2, question 20. |
The correct answer is third. |
Comment: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is carried out only if the victim has no signs of life. Signs of life are the presence of consciousness, pulse and breathing. If at least one of the signs of life is present, resuscitation is pointless, and its implementation can cause harm to a person’s health.
TICKET 3. Question 20
| What information must be provided to the dispatcher to call an ambulance in case of a road traffic accident (RTA)? Ticket 3, question 20. |
The correct answer is third. |
Comment: When calling an ambulance, it is necessary to provide information that will ensure the speedy arrival of doctors at the scene of an accident and the provision of the most effective assistance to victims. To do this, it is necessary to indicate as accurately as possible where the accident occurred and set clear landmarks on the ground. Reporting the number and general condition of the victims will allow you to make the right decision about how many ambulance teams and what qualifications should be sent to the scene of the incident.
TICKET 4. Question 20
| How should you place your hands on the victim's chest when performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation? Ticket 4, question 20. |
The correct answer is the second one. |
Comment: The human heart is located in the middle of the chest: behind the sternum, 2 fingers above its xiphoid process (the triangular bone with which the sternum ends). Performing chest compressions requires a lot of physical effort, so it is performed with both hands, which are placed one on top of the other. To prevent fractures of the sternum and ribs, these efforts should be directed along the axis of the sternum (thumbs pointing to the chin and abdomen).
TICKET 7. Question 20
| What is the optimal position for a conscious victim if a spinal injury is suspected? Ticket 7, question 20. |
The correct answer is the second one. |
Comment: The greatest danger in spinal injuries is the threat of damage to the spinal cord, which can occur with the slightest movement of the spinal column. Therefore, a victim with such an injury should absolutely not be moved or turned. To avoid damage to the cervical spine when moving the head, the neck must be secured with a homemade splint. If there is no splint, the neck is wrapped in a thick layer of cloth or a long scarf.
TICKET 8. Question 20
| How to provide first aid for frostbite and hypothermia? Ticket 8, question 20. |
The correct answer is the second one. |
Comment: In case of frostbite and hypothermia, it is necessary to minimize heat loss from the surface of the victim’s body. For this purpose, the affected areas of the body are insulated and immobilized, the victim is wrapped in warm clothes or a blanket, given a warm drink, and moved to a warm room. Giving alcohol in the cold is strictly prohibited, since first of all it dilates the blood vessels of the skin, increasing the release of heat by the body.
TICKET 10. Question 20
| What is the first aid for a traumatic brain injury accompanied by a wound to the scalp? Ticket 10, question 20. |
The correct answer is the first one. |
Comment: To stop bleeding when the head is wounded, a sterile pressure bandage is applied to the wound, and cold is applied to the wound area. A cervical splint immobilizes the victim’s head from unwanted movements. Since with head injuries there is always a suspicion of a concussion or contusion of the brain, which is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting, the victim should lie on his side.
TICKET 12. Question 20
| How should the victim be positioned if he loses consciousness and has breathing and circulation to provide first aid? Ticket 12, question 20. |
The correct answer is third. |
Comment: An unconscious victim should always lie on his side so that the root of the tongue, sunk into the larynx, does not block the airway and cause suffocation. The “recovery” position provides that the victim’s legs are bent at the knees and slightly pressed to the ground, and the back of his hand is placed under his cheek.
TICKET 13. Question 20
| For how long can a hemostatic tourniquet be applied? Ticket 13, question 20. |
The correct answer is the second one. |
Comment: A hemostatic tourniquet temporarily deprives the tissues located below the site of its application of normal blood supply, which leads to their necrosis. In the cold season, when blood vessels are already narrowed, this can happen faster. Therefore, in winter the tourniquet should be applied for a shorter period than in summer.
TICKET 15. Question 20
| What kind of injuries to the victim may be indicated by the “frog” pose (legs are bent at the knees and spread apart, and the feet are turned with the soles facing each other) and what first aid should be provided? Ticket 15, question 20. |
The correct answer is the second one. |
Comment: The “frog” pose is not related to injuries to the lower leg, ankle and foot - it is typical for injuries to the pelvis, lower spine and abdominal cavity. These injuries pose a great danger to human life and health, so they should not be aggravated by trying to change the position of the victim. In such cases, splints are not applied. First aid consists of fixing the “frog” pose, for which you need to place soft tissue rolls under your knees. It is also advisable to apply cold to the victim's stomach.
TICKET 16. Question 20
| How to determine whether a victim who has lost consciousness is breathing? Ticket 16, question 20. |
The correct answer is the second one. |
Comment: In a unconscious victim, breathing may not be detected due to the retraction of the tongue, blocking the flow of air into the respiratory tract. Therefore, to determine the presence of breathing, it is first necessary to restore the patient’s airway. To do this, you should put one hand on his forehead, and with two fingers of the other, raise his chin and throw back his head. Then, leaning towards his face, listen to his breathing for 10 seconds, try to feel the exhaled air with your cheek, determine the presence or absence of movement of the chest
TICKET 19. Question 20
| What needs to be done to remove a foreign body that has entered the victim’s respiratory tract? Ticket 19, question 20. |
The correct answer is third. |
Comment: A foreign object entering the respiratory tract causes suffocation and can lead to death within 2-3 minutes. To extract it, it is necessary to use special techniques that will not cause harm to the victim. Strikes with the heel of the palm between the shoulder blades in the direction of the neck are allowed. If this does not help, then you need to grab the victim from behind, press your chest against his back, clench your hand into a fist, clasp the fist with the other hand and apply several sharp and strong pressures on the upper abdomen in the direction of the chest.
TICKET 21. Question 20
| What are the signs of bleeding from a large artery and where does first aid begin when it is injured? Ticket 21, question 20. |
The correct answer is the second one. |
Comment: Large blood vessels - arteries - are filled with blood, which is rich in oxygen and therefore has a bright scarlet color. When an artery is damaged, rapid blood loss occurs, which can be fatal for the victim. In this case, blood is ejected from the wound in a pulsating stream. In such cases, you must immediately apply a hemostatic tourniquet 3-5 cm above the wound site. The tourniquet should be placed on a fabric lining and tightened with such force that the bleeding stops and the limb below the tourniquet turns pale. A blue limb indicates that the tourniquet is tightened too tightly.
TICKET 24. Question 20
| Is it allowed to give medications to the victim when providing first aid? Ticket 24, question 20. |
The correct answer is the second one. |
Comment: There are no medicines in the car first aid kit, since according to current legislation they are prohibited from being used in first aid. It is even more dangerous to give medications to an unconscious victim, since he does not have a swallowing reflex and any liquid or solid substance can enter the respiratory tract rather than the stomach.
TICKET 25. Question 20
| How to stop bleeding when a vein and small arteries are injured? Ticket 25, question 20. |
The correct answer is the first one. |
Comment: When veins and small arteries are injured, blood loss is not threatening and does not require the application of a hemostatic tourniquet. In such cases, a layer of sterile bandage is applied directly to the wound, a large amount of cotton wool or another rolled-up bandage is placed on it, after which the wound site is tightly bandaged - a pressure bandage is obtained.
TICKET 29. Question 20
| What are the initial steps to take when providing first aid in the event of an injury resulting from a road accident? Ticket 29, question 20. |
The correct answer is third. |
Comment: First aid for wounds is aimed at avoiding complications during wound healing, in particular, infection entering the body. Do not wash the wound, apply cotton wool to the damaged area or treat it with ointments. Antiseptic agents (iodine, brilliant green, etc.) can only be used to treat the skin around the wound. Apply a sterile napkin from the motorist's first aid kit to the wound itself, and use a bandage or tape to secure it. This work should be performed with medical gloves, which are first wiped with alcohol, cologne or unleaded gasoline.
TICKET 32. Question 20
| How to ensure restoration of the victim's airway when preparing him for cardiopulmonary resuscitation? Ticket 32, question 20. |
The correct answer is the first one. |
Comment: After cleaning the mouth, the best airway patency, facilitating artificial respiration, is ensured when the victim lies on his back with his head tilted back (if there is no damage to the cervical spine). To carry out artificial respiration using the mouth-to-mouth method, the victim’s lower jaw must be pushed forward. After this, access to the oral cavity will open.
TICKET 34. Question 20
| How is cardiopulmonary resuscitation performed on a victim? Ticket 34, question 20. |
The correct answer is third. |
Comment: When clinical death occurs, maintaining blood supply to vital organs is of primary importance. Therefore, cardiopulmonary resuscitation should begin with chest compressions, which is rhythmic and sharp manual pressure on the victim’s sternum, simulating the work of the heart. After 30 compressions, you can pause for a short time to take two breaths of artificial respiration, and then immediately resume chest compressions. Resuscitation cycles are repeated one after another, without stopping, until signs of life appear or until the ambulance team arrives.
TICKET 37. Question 20
| How is first aid provided for broken limbs if there are no transport tires and available means for their manufacture? Ticket 37, question 20. |
The correct answer is the second one. |
Comment: In case of fractures of the extremities, it is necessary to ensure complete immobility (immobilization) of the broken bones. If it is not possible to apply a splint, then the broken arm is carefully bent at the elbow and suspended from the neck using a scarf. For reliable fixation, the arm in this position is bandaged to the body. When a leg is broken, it is bandaged along its entire length to the other leg, after placing soft tissue between the legs to avoid disruption of the blood supply from prolonged compression. The bandaging at the fracture site should not be tight.
TICKET 38. Question 20
| In what cases should the victim be removed from the car? Ticket 38, question 20. |
The correct answer is the second one. |
Comment: A victim in an accident can be removed from the car until doctors or rescuers arrive only in cases that pose an immediate threat to his life. Such cases include the onset of clinical death, that is, the simultaneous absence of consciousness, pulse and breathing. Since resuscitation in a sitting position is not possible, the victim must be carefully removed from the vehicle and placed on a hard, horizontal surface.
TICKET 40. Question 20
| What is first aid if there are signs of a superficial thermal burn (redness and swelling of the skin, the formation of blisters filled with clear liquid at the burn site, severe pain)? Ticket 40, question 20. |
The correct answer is third. |
Comment: An attempt to open blisters, remove remnants of clothing, wash, lubricate or bandage the burn site can cause painful shock in the victim. Therefore, without treating the burn site, you need to cover it with a sterile napkin to avoid infection. To alleviate the condition of the victim, he is given painkillers that do not cause allergies, warmed up and given plenty of drinks of any kind. After applying the napkin, you need to carefully apply cold to the burn site.
Download tickets for PMP
Download the first aid manual for drivers
Memo on providing primary care
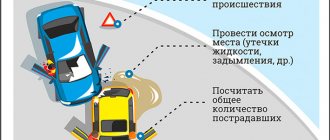
Providing first aid in case of an accident
Each specific case has its own algorithm of actions.
Help with clinical death
How to check that a person is in such a critical situation? You need to check the pulse in the carotid artery and try to bring him to consciousness. When a heartbeat cannot be heard and a person does not regain consciousness, we can speak of clinical death.
How to help:
- Check whether the victim has fractures in the sternum. To do this, just run your hand over the body.
- Strike the chest as quickly as possible when there are no injuries.
- If you feel where the bone is broken, you should not hit, but push in the chest.
- In the case of coma, the criminal code does not provide for any punishment, so do not be afraid to act to save the person’s life by all possible means.
- After a blow to the sternum, the passenger or driver must be evacuated. It is best if there is an assistant nearby. Then the person should be taken from both sides (one by the arms, the other by the legs).
- Lay the victim on his back, preferably on a flat surface.
- Start breast massage.
Help with bleeding
- Determine the type of bleeding: capillary, venous, arterial.
- In the easiest case, you just need to disinfect the wound and apply a sterile bandage.
- In case of venous bleeding, it is important to elevate the injured limb, so the blood flow will slow down. Apply a bandage and tie it tightly. If there is a lot of blood, tie a tourniquet above the wound.
- How to distinguish arterial from venous? The first flows in a thin stream and pulsates. Such an injury is very dangerous and may not be compatible with life if first aid is not provided. Bleeding can be reduced by squeezing the artery located above the wound. Bandage in this place with any available object (homemade flagellum). Record the application time and bandage the wound itself with a sterile cloth. You can remove the bandage no later than after two hours, otherwise tissue death will begin.
Help with a fracture
- To examine the person’s body, to do this you need to feel with your hand the soft areas where the injury occurred.
- Remove clothing at the fracture site if necessary.
- Ask if there are any complaints.
- You can't be allowed to stand up.
- If you have a first aid kit, you can inject an injection of painkiller near the injury site.
- If the fracture is accompanied by an open wound, the bleeding must be stopped and the wound disinfected.
- Immobilize the broken limb.
- Apply a custom-fitted splint to several joints at once directly onto loose clothing.
Help with burns
- If a car with a passenger in it catches fire, you must immediately try to rescue the person, extinguish the burning clothes he is wearing, remove or cut them.
- Apply ice compresses to the burned areas.
- Cover the affected area with a sterile bandage.
- If the wound is shallow, you can moisten a cloth with alcohol.
- Give an anesthetic injection or give the drug in tablet form.
- Do not: wash the burned area, touch it with your hands, or lubricate it with oils.
- Give the victim plenty of clean, still water.
Help with loss of consciousness
- Due to stress or heat, the driver may become ill while driving and lose consciousness. First, you need to check the person’s condition, feel the pulse, and observe breathing. If the listed signs are absent, you need to do direct cardiac massage.
- If there are signs of life, then you need to put the victim on a level place, put something under his feet so that the blood flows to the head. Unfasten the top buttons on your clothes, loosen the belt on your waist, give more oxygen. An effective method is the vapor of ammonia, which must be inhaled by the participant in the accident.
- If these measures do not help within 3 minutes, then you urgently need to shift the victim onto his stomach and apply a cold compress that is on hand (for example, a bottle of ice water) to his head.
- While the ambulance is traveling, you need to monitor signs of life (pulse, breathing).
Help for seizures
Epilepsy is accompanied by symptoms such as convulsions, wide pupils, involuntary urination and others.
- Place your head on some object.
- Loosen your tie or undo the top buttons.
- Turn over on its side and note the duration of the seizure state.
- Shoulders should be pressed to the ground.
- Insert any medium-sized object into the mouth between the root teeth to prevent the tongue from recessing.
Breathing problems
- Such problems include choking, severe coughing, redness of the scalp, and severe vomiting. In such a situation, you can save a person in only 3 minutes.
- You need to hit the victim on the back between the shoulder blades.
- Fold his hands so that they are above the epigastric region. Fold your limbs into a lock and place them below. Press with your hands.
- If the participant in the accident is unable to cough in order to get rid of the foreign object (lost consciousness), you need to put him on his back and press with a sharp movement on the epigastric region.
Chest pain
- The chest can be easily bruised during a traffic accident. In this case, after calling medical workers, you must give pain relief and ensure complete rest.
- Apply ice or something cold to the sternum.
- Watch for signs of life and make sure the person doesn't lose consciousness. Talk to him, ask about his health.