Advertisement
Today, a large percentage of motorists treat the seat belt quite calmly and even skeptically. This is due to the fact that in the modern world there are too many things, including protective equipment - a person involuntarily begins to underestimate what he has known for a long time and has already become something commonplace.
In fact, the seat belt is an excellent means of protection, which is why it is inferior to other developments and has been serving people for about two centuries.
A seat belt is a means of passive protection for the driver, passengers and vehicle. Its main function is to hold the passenger in the most static position during emergency braking (due to an accident or simply sudden braking).
Advertisement
Due to a rather passive attitude towards seat belts, people forget how to fasten a seat belt correctly and sometimes even do it in principle. We will talk about the nuances of “interaction” with a seat belt, its purpose and structure in this article.
Design features and varieties
Seat belts began to be installed on cars at the dawn of the automotive industry. The first attempts to develop a simple protection device were made at the very beginning of the 20th century, but at that time they did not show decent results, and continuing research in this direction became impractical.
The second round of interest in this type of security mechanism appeared in the last century. The device was offered as an additional option, and not a mandatory element of the entire car design. Only after some time the strap began to be installed as basic equipment.
Automotive researchers have considered replacing belts entirely, and alternatively using only panel-firing airbags. But numerous tests have shown the low effectiveness of using pillows independently, as opposed to using them together.
Now seat belts (SB) have become an integral part of any car, which allow you to keep passengers in the seat, regardless of the emergency situation that has occurred.
The main component of the passive safety device is fibrous polyester tape. This material has characteristics that allow it to withstand high loads and is also less susceptible to mechanical stress and tearing. The strap holds the body in a fixed position, preventing it from moving forward in a frontal collision.
Another important fact is that the RB prevents the possibility of a motorist or passengers inadvertently flying out of the vehicle, and also ensures the impossibility of a collision with the structural elements of the car.
A complete RB design includes:
- fixed and movable safety equipment attachment points;
- lock;
- reels that have an inertial tension function that allows you to move smoothly on the seat;
- limiters;
- pretensioner
The above elements appeared as the automotive industry developed, and even today, not all cars have a passive safety system that combines each of them at the same time.
Useful tips
There are several guidelines to follow when using seat belts:
- Do not install special plugs on the belts so that the car’s security system does not bother you with an audible warning. Firstly, we are talking about the safety of many people, and secondly, if a traffic inspector notices such “tricks”, then a fine cannot be avoided. In addition, if the car’s computer “thinks” that the seat belts are fastened, then in the event of a strong push, the airbags are guaranteed to deploy.
- If there is a child in the car, then it is not enough to limit yourself to a car seat that is simply placed in the back seat. First of all, it must be equipped with its own seat belts. Also, the chair must be securely fixed.
- You should not buy or use belts that show scuffs and other damage. In an emergency, they can simply burst. If it is not possible to replace them, then you should contact a service station and carry out at least a temporary repair of the products.
- You can replace the belts yourself, but it is better to contact a service center, since an inexperienced driver may perform the installation incorrectly.
- You should not use additional protective equipment that is not provided by the car. This may cause the security system to malfunction.
- It should be borne in mind that the tapes of the new belts are much more elastic. When hemming such products with a needle, you need to completely repeat the factory seams, even if it seems that it would be better to make new ones. For stitching, you can only use strong nylon thread.
It doesn’t matter at all whether a person is driving along a remote country road or along a busy highway. The danger of colliding with another car or any other objects is always present. Therefore, do not neglect seat belts. Modern models are convenient, and it takes no more than a few seconds to fasten the tape. You shouldn't skimp on belts either. It is better to buy new products from the car manufacturer or other recommended companies.
Types and distinctive features
The key criterion by which RBs differ is the number of fixation points. This parameter is of fundamental importance and helps to minimize injuries during an accident.
The following types of RB exist:
- point-to-point,
- three-point,
- four-point,
- five-point,
- multipoint.
It is important to note that the number of fixation points often makes the use of a safety belt insufficiently comfortable, but increases the likelihood of injury.
2-point
The two-point seat belt was one of the first to be installed on production vehicles (TS). The effectiveness of this type showed the least results. In total, 2 types of RB such fastening systems are provided.
In the first option, the passenger is fixed in the lumbar region transverse to the seat. One mount was located in the sill or side pillar area, and the other was located between the front seats. For the convenience of fixing the RB, the security system included a lock with a latch.
The disadvantage of the design is that the strap only held the lumbar region, and in an accident the person continued to move the upper part of the body by inertia in the direction of the steering column or panel. Thus, it is simply impossible to avoid injury, although it is possible to keep the body from flying out.
The option with a chest strap provided for the installation of fasteners on the side pillar and between the front seats. In the event of a collision, the RB guaranteed the retention of the body, but the likelihood of the person fastened slipping under the belt increased, which also contributed to the high incidence of injuries.
Pros and cons of different seat belts
Two-point seat belts can still be found in the back seat of some cars. They were equipped with outdated Russian car models. There are both waist and shoulder versions of such belts.
The lap belts look like safety belts on airplane seats. They do not restrict movement, but can cause severe spinal injuries and even lead to paralysis.
The shoulders are fastened diagonally. The top point is located on the central pillar of the side of the cabin. The lower one is a lock installed between the passenger and driver's seats. This type of belt is not reliable enough, since a person can “emerge” from it in an accident.
Three-point seat belts are installed on almost all modern cars. The V-shaped diagonal-waist design promotes uniform distribution of the energy of inertial movement between the parts of the torso.
Four-point seat belts are equipped with sports car models, the seats of which have four attachment points. Together with five- and six-point ones, they represent the group of the most reliable seat belts, but cannot be installed on ordinary cars due to design features.
Static seat belts are not installed on modern car models. The wide strap that forms the basis of such a belt is a piece of synthetic tape of a certain length, which is manually adjusted. This design does not meet modern safety requirements.
Dynamic seat belts are equipped with a special mechanism that evenly extends or retracts them with smooth movements of the passenger. With a sharp jerk, the belt is fixed, due to which the person’s body is held tightly in the seat.
The timing belt mechanism is closely connected and works in conjunction with all other safety systems of the machine. The electronics with which the car is equipped, based on sensor readings, tightens the safety belts in advance and securely fixes them in the event of dangerous situations. If the machine successfully avoids the danger, the belts return to normal operation. The most modern cars are equipped with this most advanced and reliable mechanism today.
3-point
Most modern vehicles use three-point seat belts, given that such a system is considered the most practical to use and eliminates the possibility of further movement of the fastened person in a collision due to inertia.
This type of design has three clamps - two points in the side pillar, and 1 with a lock between the seats.
The mounting point on the side of the vehicle pillar is fixed, and the other is equipped with a coil to automatically return the vehicle to its original state. A movable lock tongue is attached to the RB for easy fixation of the seated person. This design combines two types of 2-point seat belt at the same time.
The sliding tongue for the lock allows you to sit comfortably in the seat and, in one motion, secure your body in a stationary state in case of an emergency.
Seat belts for children and pregnant women
The effectiveness of seat belts is determined by the most important factor - our own life and health, as well as those who are in the car with you.
Proper protection from harm for those who especially need guardianship protection is also an important factor. We are, of course, talking about the youngest passengers, as well as pregnant women who, due to the physiological characteristics of their bodies, cannot count on the safe use of conventional 2-point or 3-point seat belts. Many people ask at what age can children use a seat belt. The fact is that a person must wear a seat belt, regardless of age, but the youngest require special equipment for this. Children under twelve years of age must be transported in a vehicle in child seats equipped with multi-point lap belt systems, and which must be specially selected for the weight and height of the child. As in the case of an older passenger, failure to use seat belts to restrain children is fraught with criminal liability and a fine depending on the circumstances.
As for special seat belts for pregnant women, there are many analogues in car stores. Their secret is that the load is distributed from a different angle, without damaging the stomach or causing significant damage in the event of a dangerous situation.
Seat belts for pregnant women allow you to relieve the usual places, while protecting the health of both the fetus and the mother.
4-point
The four-point mounting system is rarely used on budget or low-performance cars, and is often only seen on racing or sports vehicles.
Due to the inconvenience of use, it is not widely popular. The attachment points in such a device may vary. One of the types includes vertical straps with a fixed one-piece fastening and one detachable one in the lumbar area. A special feature of this system is that the vertical straps are not attached to the structural elements of the body, but directly to the seat.
Before getting into cars, you will first need to put 2 straps over your shoulders, after which you need to stretch and secure the lumbar belt.
The second version of the system provides fixed vertical straps that can be freely detached. Each of them has a tongue for installation in the lock.
Types of modern seat belts
As seat belts began to be introduced into the automotive industry, manufacturers began to offer different types of these devices. As a result, in modern cars you can find several categories of belts:
- Two-point belts are an obsolete option. Such devices are most common in passenger buses and airplanes. Sometimes two-point belts are installed in the rear seats of cars for the passenger sitting in the middle.
- A three-point belt is an option familiar to most car owners. It is also called diagonal-waist. It has a secure fit and is universal (suitable for both the front and rear rows of seats in any car).
- Four-point harnesses are not a widely used type. Most often they are used on sports cars, special equipment, and sometimes on SUVs. The belt is attached to the seat at four points, keeping the person from tipping over or getting hit hard.
- Five-point belts are used only in expensive supercars, as well as in the design of child restraints. In addition to the shoulder and waist fastenings, another belt is installed, located between the passenger’s legs.
Four-point belts can be found in racing cars and sports cars.
5-point
Five-point seat belts, like the previous type, are widely used in sports vehicles, as well as in car seats for children.
In terms of its structure, it is the same 4-point belt with an additional strap. The auxiliary element is located at the bottom of the seat - between the legs, and is placed in a special lock.
This type of protection guarantees the most reliable retention of the body, and also allows you to distribute the load evenly across the belts.
What can you pay attention to when choosing a belt?
- Components. It should be noted that each car has an individual security system structure, which may differ on different models.
- Fasteners The fundamental element in the passive safety system is the fastener, since it ensures the strength of the structure. Fasteners are mounted on body elements, since at the moment the body moves by inertia with acceleration, a colossal impact is exerted on the belt.
If the fastenings were mounted in the seat, then excessive loads could simply destroy the integrity of the structure, since the backrest moves along with the body.
When installing the mount into the body, such displacement cannot occur. The exception is cases when the impact leads to a total violation of the integrity of the body. The fastening system may provide for fixing the belt directly into the seat. This design is typical in sports cars, where the seats for the driver and passenger initially provide for the impact of enormous loads, for this reason such fasteners are possible. The lumbar belt is attached exclusively to the body.
4, 5 and 6 point...
There are also four-point designs. They are attached with the upper pair of points to the back of the seat, and the lower pair - directly to the chair itself. Their design is inconvenient for ordinary drivers, but they are widely used in sports cars.
Five-point. They are also equipped with sports cars.
This type is also familiar to many parents who have to travel with children. After all, it is five-point structures that are used in children’s car seats, where the child is securely secured with three straps at once. Two are located vertically, and the third is at the bottom, passed between the legs and inserted into the fastening that connects all the straps.
In general, with regard to the transportation of children under 12 years of age and the use of standard equipment, the Traffic Rules clearly regulate this issue, defining only child car seats and boosters as the only permitted devices. As for special children's seat belts and various adapters, the rules do not say anything about them, so their use may lead to a fine. But in combination with approved devices, they can and even should be used, because there can never be too much safety for a child.
Six-point. You won't see them on regular cars. Racing cars are equipped with such designs, where even the driver is called a pilot, and the driving itself is called piloting.
They have a rigid fixation and ensure that the driver is literally chained to the pilot seat.
Ease of use
Speaking about ease of use, it should be noted that vertical belts are suitable for a person of any build and height, in contrast to belts with a diagonal attachment point in the body.
A diagonal belt with fastening in the body can pass almost in the neck area of a short driver. This circumstance indicates not only inconvenience, but also unsafe operation, since at the moment of a collision the inertial force and tension of the belt will act on the person’s neck. This results in a high probability of injury and significant harm to health.
For tall people, a diagonal position of the belt with an attachment point in the body is also not always suitable, since the strap passing below the shoulders can significantly restrict the movements of the arms.
Manufacturers of modern cars have taken care of this and have provided the possibility of moving the body mount in height for optimal adjustment to the seated person.
Lock part
The detachable design element of the fastening point provides a convenient location of the seat belt straps.
The principle of operation is simple - a metal tongue with a hole, attached to the belt, is inserted into the lock hole and secured with a pin to fasten the structure. There is a button on the lock body that retracts the pin and separates the elements.
The key to the effective operation of the entire passive safety system is the correctly adjusted RB tension. Previously, each driver or passenger was required to adjust the straps to suit their body size. If the driver had to do this quite rarely, then the passenger must carry out the adjustment constantly.
With the advent of inertial reels in the design, the issue of constant belt length settings was resolved forever. The car seat belt device automatically tensioned the belt so that the passenger or driver could fit comfortably in the seat.
The main feature of the reel is the function of blocking the belt if you try to sharply pull the tape out of the device. The mechanism will not allow you to quickly unwind the coil, preventing the person sitting in the seat from shifting due to inertia when the car suddenly stops.
The inertial coil performs 3 main functions:
- provides the necessary belt tension, adapting to the body composition of the seated person;
- automatically collects the belt after it is unfastened;
- prevents involuntary movement of the body during sudden braking or stopping.
There is also a drawback - the mechanism technically does not have time to instantly respond to sudden tension. This allows the body to speed up a bit in an emergency, which significantly increases the likelihood of injury.
The best seat belt manufacturers
Of course, it is best to use original belts, that is, from the car manufacturer. But often car owners prefer to save money or want to install more reliable four-point models.
Healthy! There is no point in purchasing used belts. There is a risk that they will fail in a few months or are simply no longer able to perform their main function (for example, if the tape has already been greatly stretched and has lost its elasticity).
If we talk about seat belt manufacturers, it is worth highlighting the following brands:
- Sandtler. A large German manufacturer of auto parts and various accessories for cars.
- Prosport. Production is located in Taiwan. The company produces sports and regular belts of various types.
- Schroth. Another German company that produces belts not only for cars, but also for public transport and airplanes.
- Monza. Italian manufacturer of belts and accessories.
The belts should also come with fasteners and instructions. There are a few more features that are worth paying attention to.
Limiters
The main function of the limiter is an insignificant and smooth increase in the length of the seat belt.
During emergency braking or a collision, the body continues its inertial movement, being subjected to significant overloads. Seat belts that are not equipped with limiters instantly stop the vector of movement, injuring the chest, neck or lumbar region of a person.
A gradual and smooth increase in the length of the belt allows you to reduce the speed of inertial movement, while reducing the likelihood of injury.
The limiter has the form of a torsion bar, which acts as an axis for the coil. When triggered, the reel stops the unwinding of the belt, the body rests against the belt, creating a load on the belt.
Pre-tensioner element
Pretensioners began to be installed in seat belt designs several years ago, but their role should not be underestimated. As noted earlier, the reel cannot technically stop the unwinding of the belt instantly, which is why the body still manages to continue its inertial movement. It is to prevent this drawback that pretensioners were developed, tensioning the belt until the moment of a sharp stop and inertial movement of the body.
There are 2 main types of pretensioners.
- Squib cartridges.
- Electrically driven.
Here, the mechanical principle of operation alone is no longer sufficient. Advance tension of the belts is ensured by the activation of additional shock sensors that send a signal to the control unit, which are equipped in modern cars.
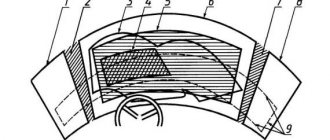
Car seat belt device
The design of seat belts is both simple and reliable. It includes straps, mounting bolts, lock and retractor. For the manufacture of straps, various synthetic materials are used, which affect the strength.
Many older car models are equipped with an inertia mechanism, due to which the belt can be slowly pulled out to the required length from the reel, allowing the driver freedom of movement. In the event of a collision, the belt is sharply pulled out, which triggers the lock, blocking the reel from further unwinding. This mechanism has a significant drawback. If bulky winter clothing creates a large space between the person's body and the belt, the effectiveness of the inertial mechanism is greatly reduced, which can cause serious injury.
You can learn about the types of airbags and the features of their operation from this material.
How to make a Scandinavian light for your car - see here.
A more advanced design of belts with pretensioners has appeared quite recently. Cars equipped with pretensioners are the safest. During an accident, the passenger's body is pressed tightly against the seat. The first pretensioners used pyrotechnic cartridges, but with the development of technology in the latest car models, they are increasingly being replaced by electric actuators. These pretensioners operate silently. Moreover, unlike squibs, they are reusable. Manufacturers often combine these two types of pretensioners in one seat belt mechanism. In this case, the decision about which one to use is made electronically based on data from the sensors with which the machine is equipped.
General operating principle
It will take literally 1 minute for the driver or passenger to fasten their seat belts.
As an example, let’s consider a mechanism with a three-point fixation system, due to their mass and greatest prevalence. After the driver is seated in the car seat, it is necessary to smoothly pull the belt to the required length, directing the metal tongue into the hole in the lock.
Having heard the characteristic sound of a latch, you can release the belt, allowing the inertial reel to remove the excess length.
If the structure is equipped with pretensioners, then in an emergency it is they who begin their work:
- in the event of a collision, sensors located in the nose of the car will transmit the relevant information to the on-board computer, which activates the pretensioners to tighten the straps;
- As the load increases, the torsion bar comes into play, successively increasing the length of the strap to dampen acceleration.
If the design does not provide for the presence of the element in question, then their task is performed by the coil together with the torsion bar.
How to use seat belts
Operating a seat belt is quite simple; any motorist and even a young passenger can handle it. At the same time, you need to know about a number of important nuances:
- To check that the seat belt has sufficient tension, you must insert your hand between the belt and your body. The presence of compression indicates that the device is tightened well;
- Do not allow the belt to twist. In this case, it will not be able to work correctly during a traffic accident;
- After a serious accident, it is imperative to check the condition of your seat belts. In particular, the strength of the tapes and the reliability of fastening to the body;
- Seat belts need to be changed every 5-10 years, as they gradually wear out.
It is worth remembering that under no circumstances should you loosen the tension belt, even if it hinders movement. Otherwise, the tape will lose its braking properties, which will reduce its effectiveness. According to statistics, if a person is not wearing a seat belt, then the risk of injury increases:
- five times when the vehicle rolls over;
- 2.5 times in a head-on collision;
- 1.8 times when hitting the side of the car.
Recommendations
No one can ever know when an accident will happen. An analysis of a huge number of videos of road accidents suggests that the survival rate in serious accidents is many times higher for passengers who were using the RB at the time of the accident.
Situations cannot be ruled out when an unbelted driver simply flew out of the vehicle at the moment of the first impact, which saved his life, taking into account the likelihood of the vehicle subsequently moving along an unpredictable trajectory or overturning.
It is important to note that fastening your seat belt before driving is one of the requirements of the Russian Traffic Regulations, for ignoring which a fine is provided. This obligation is fully justified, since in many road accidents the cause of serious injury or death is the unfastened vehicle.
Another reason why you should spend 10-15 seconds on a passive airbag system is the likelihood of getting a concussion, a broken nose, or other damage to the area of the body that comes into contact with a deployed airbag, even in a minor accident.
It should be noted that the opening speed of the PB is more than 300 km/h. Add to this value the speed of inertial movement and the final result is a very noticeable blow, in which loss of consciousness will be the least consequence.
Innovations in passive safety
The world's leading automakers are working every day to improve all vehicle safety systems. A relatively recent innovation is pretensioners, but they are no longer new.
Innovative belts that simultaneously serve as airbags are already being actively tested.
The essence of the system is to instantly fill the belt with gas, which allows you to increase the area of contact between the belts and the body, as well as evenly distribute the load, reducing the likelihood of injury.
More expensive vehicle models in the future will be equipped with self-adaptive pretensioning systems that independently adjust to the physical parameters of the seated person. The computer calculates the required force to hold the body at the time of the accident.