What is traceological examination
The study of traces at the scene of a road accident is carried out as part of the investigation into the circumstances of the emergency. Drivers who do not know what a forensic examination after an accident is, have no idea about the features of a transport inspection. The study is aimed at analyzing tire prints. Complex calculations make it possible to recreate the mechanism of a traffic incident and establish the sequence of actions of motorists and the cause-and-effect relationship between driving and the results of the collision.
Trace examination after an accident is a study of traces and prints left at the scene of an accident, carried out to determine their nature of occurrence and affiliation. By sequentially performing complex calculations, the expert recreates the mechanism of an accident and establishes the sequence of damage to objects.
Thus, the main goal of this study is to restore the complete picture of the incident.
Traceological examination is carried out in controversial situations when it is necessary:
- to recreate a picture of the actions of drivers, the final result of which was a traffic accident;
- find out whether the vehicle under investigation was present at the scene of the incident;
- determine whether the damage present on the vehicle corresponds to the circumstances of a particular traffic accident;
- prove that there was no fault of a specific person in creating the emergency situation;
- receive from the insurance company a larger amount to compensate for losses than it agrees to pay.
What is it prescribed for?
Reasons for ordering a trace examination:
- The emergence of disputes with the insurance company regarding payment of compensation after an accident . Often insurers try by any means to minimize the amount of compensation, so the opinion of an independent expert will help restore fairness in resolving this dispute.
- Calculation of the main culprit of a traffic accident .
To resolve this situation, the court orders an independent examination. For example, it is impossible to do without trace analysis in cases involving changing lanes of cars that were traveling in the same direction. Both participants in the accident can claim that there was no change in their movement, and also that the opponent changed lanes, violating the requirement of the Russian Traffic Regulations to give the right of way to the car driving straight. In this case, trace experts will determine the presence of traces at the scene of the accident and the instigator of the accident. - A dispute over compensation - the payment that must be made by the instigator of the accident to the injured parties. Situations often occur when victims claim that certain dents appeared during a collision, when in fact they have been there for a long time.
- Carrying out an identification comparison of traces of the incident with the submitted samples .
For example, traces of enamel left by a vehicle that fled the scene of the accident were removed from a damaged car. An investigation into this case was carried out, and after a while a car was found with a similar enamel peeling. A traceological expert study will compare and determine the involvement of the detained vehicle in this accident.
Thus, the main task of traceological examination is to determine the cause of the accident. An inspection can be scheduled on any day of the incident proceedings, but it would be more correct to conduct it at the stage of preliminary investigation. It is at this time that the determination of the culprit of the accident will be most correct and accurate.
In what case is it prescribed
Traceological examination after an accident is carried out to reconstruct events, if there is a discrepancy in the testimony of participants in the accident and eyewitnesses, to prove the driver’s guilt, to determine whether the damage on the car corresponds to the circumstances of the incident, to establish the mechanism of the collision, and to appeal the verdict.
Law on carrying out
Traceological testing is carried out on the basis of several regulatory documents, which also determine the procedure for its implementation. They are:
- Law “On state forensic activity in the Russian Federation”.
- Criminal Procedure Code, Chapter 27, Art. 195 – 207.
- Code of Civil Procedure, art. 79 – 87.
- Arbitration Procedure Code Art. 82 – 87.
- Code of Administrative Offenses, Art. 26.4. – 26.5.
Each regulatory document regulates questions about the purpose, procedure, commission and comprehensive examination, and its conclusion.
Important information about trace examination
Traceological examination is classified as a subtype of forensics. This research allows you to find and, if possible, identify traces left by an object in a certain situation, as well as find out the mechanism of their occurrence. In most cases, it is used during operational activities, the activities of investigators and interrogators, or appointed by the court.
The need for an examination
Such examinations are not carried out in every accident and are considered a rather rare occurrence. Expertise is of little use when there are other open and accessible sources of information. However, sometimes there are no witnesses to an accident, and people are injured as a result of the accident. Naturally, no one will conduct an examination in the event of a collision between two drivers who independently agreed with each other. First of all, examination is necessary to investigate an offense or crime when the rights and interests of citizens are affected and violated. At the same time, not every offense is investigated; for example, it is unlikely that examinations will be carried out in cases of violation of the rules for driving through an intersection.
IMPORTANT !!! Most often, experts are involved when there are injured or dead people, which is typical for serious offenses or crimes.
By conducting an examination, witness testimony can be clarified when it diverges, and there is no other way to obtain information. Based on the conclusion obtained, you can find out a lot of information about what happened, even when there were no witnesses.
Questions to the expert
Conventionally, questions asked to trace experts on the topic of the research being conducted can be divided into two groups:
- identification;
- diagnostic.
Typical questions of the first group are:
- Do the traces left at the scene belong to one or more objects?
- What objects left the traces found?
- Could the marks left behind have been caused by a car whose involvement in the accident was proven?
- Are the marks and damage left behind the result of the accident in question?
The list of typical diagnostic questions is as follows:
- Are there any traces at the scene of the traffic accident that are suitable for research?
- What was the trajectory of certain vehicles involved in the accident?
- What is the make of the car whose traces were found at the scene?
- How were objects, vehicles, and pedestrians positioned at the time of the collision?
- In what sequence did the collision of various objects and the formation of traces occur?
- What can be said about the mechanism of the accident in question?
The questions posed to an expert traceologist cannot go beyond the scope of his special knowledge.
The victim and the accused in the case of the administrative offense in question can also participate in the activities of the expert by drawing up questions for him that they would like to receive answers to in the expert’s conclusion.
There is a whole list of standard questions that are asked to an expert during a trace examination. Conventionally, questions can be divided into several groups, each of which depends on the object under study, goals and objectives.
Group 1 – issues related to determining the group affiliation of vehicles. Sample list:
- What type of transport do the tracks that were left at the scene of the accident belong to?
- What model of tires left the tracks that were seized from the scene of the accident?
- Do the traces left correspond to the specified type of vehicle?
- Based on the identified shapes, sizes and location of the marks on the vehicles, was it possible for the vehicles to collide?
Group 2 – is used so that during a traceological examination the whole picture can be established from the available parts. Sample list:
- Are the objects of parts that were found at the scene of an accident actually parts of a specific vehicle?
- Were the particles of paint, glass, and plastic that were found at the scene of the accident and on vehicles before the accident one whole?
- Were any of the vehicles changing lanes at the time of the collision based on the tracks found?
Group 3 – used for the purpose of identifying a specific vehicle
- Do the detected tracks belong to the specified vehicle?
- Do the tracks found at the scene of an accident belong to one or more vehicles?
- Was the trace found left by this particular car or another?
Group 4 – questions that help determine the location of an accident
- Sample list:
- In which lane did the accident occur?
- In which lane did the accident occur?
- Did the accident happen on the side of the road or on the roadway?
- How were the vehicles positioned relative to the boundaries of the roadway at the time of the collision?
Group 5 – questions of traceological examination aimed at establishing the collision process?
- At what angle did the collision occur?
- Which vehicle was moving at a higher speed at the time of the collision?
- Was the vehicle stationary or in motion at the time of the accident?
- In what direction were the vehicles moving before the collision itself?
Types and classification of trace examinations
Traceological research is carried out in relation to mechanisms, objects and living beings. The types of traceability examinations discussed below can, to one degree or another, be used to investigate the causes and circumstances of an accident:
- homeoscopic examination - the study of human traces: fingerprints, footprints, shoe prints, teeth, various parts of the body, etc.;
- mechanoscopic examination - the study of traces of objects and damage found on things, namely: tools, tools, mechanical damage to clothing, knots and loops;
- examination of locks - study of the main characteristics of locks, including their condition at the time of examination;
- examination of fillings - examination of abandoned fillings to determine their integrity;
- examination of prints of production mechanisms on objects - carried out in order to determine the relationship of the object under study to the equipment;
- transport research – study of traces of vehicles: tire prints, dents, scratches and other damage;
- study of animal prints - study of paw marks and horseshoes.
Cost of the procedure
When it comes to paying for the examination, everything will be assigned to the person who caused the incident. But this is only in the case when conducting research is mandatory and plays a significant role. But this is almost always exactly what happens.
Initially, it is the customer who will have to pay the entire amount for the examination. Subsequently, a claim is filed, which requires funds from the culprit. It is impossible to immediately and accurately indicate how much the research will cost. It all depends on the complexity of the situation, the availability of documentation, urgency, importance, etc. The average price for a traceologist’s work is 15-20 thousand rubles. A reduction occurs when there is no urgency or the entire process is simplified.
General provisions of the methodology for conducting traceological examinations
The methodology of traceological examination consists of a system of techniques, methods and techniques, as well as various technical means that are used to examine various objects and items within the framework of the examination.
Objects of traceological examination are divided into the following groups:
1) Physical evidence (traces of a crime);
2) Material conditions of the crime scene;
3) Procedural documents containing the situation at the scene of the incident (for example, a protocol for examining the scene of the incident);
4) Reference materials;
5) Samples (characterizing certain types of objects or displaying the properties of the objects being checked).
Objects of traceological examination are also divided into objects directly involved in the identification process and indirectly involved in identification.
Objects directly and indirectly involved in identification are divided into:
1) Identifiable objects in relation to which the question of identity is being resolved;
2) Identifiable objects that reflect the properties of other objects, but these objects themselves are not identified.
Identifiable objects include: people, premises, objects, animals, mechanisms, etc.
Stages of traceological examination:
1) Preliminary research;
At this stage, the expert gets acquainted with the materials received for research, inspects the objects, checks their compliance with the investigator’s resolution (description), then the expert takes photographs of the packaging and appearance of the object. After this, the expert must draw up a plan for further research.
2) Detailed research;
At the stage of detailed research, the expert will have to identify identification features of the object, which should reflect the properties of the identified object. Among the types of identification signs there are: signs of group and individual significance. Also, features are divided into general and specific; general features characterize the object as a whole (design, shape, weight, etc.), and specific features characterize the details and parts of the object.
According to the nature of the connection with the identified object, features are divided into necessary and random features.
According to the time of occurrence, signs are divided into signs that appeared during the division of the object into parts and signs that appeared before its division.
According to the nature of the assessment of frequency of occurrence, signs are divided into statistically determined and subjectively determined signs.
It is also worth mentioning the identification period, during which it is possible to identify an object by its displays. At the stage of detailed research, the experiment itself can be carried out directly, as well as comparative and separate research.
3) Evaluation of results and formulation of conclusions;
At this stage of the assessment, the expert must evaluate and compare the identified matching and distinguishing features and subsequently formulate conclusions.
The expert's conclusions must be clearly formulated and not have double meaning; the conclusions must contain a clear answer and explanation to the question or task posed. If the expert cannot solve the issue, then he must give appropriate explanations and indicate the reasons for the inability to solve the problem.
The expert's conclusions are divided into conclusions containing an answer to the question posed, and conclusions that indicate the possibility of resolving the issue.
They also distinguish between conditional and unconditional conclusions, positive and negative, categorical and probable, as well as unambiguous and alternative.
4) Preparation of research materials.
At the stage of registration of research materials, the expert draws up a written opinion in accordance with the procedural requirements arising from the requirements of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law “On State Forensic Expert Activities”. This document should be illustrated with diagrams and photographs documenting the expert findings and conclusions.
How to do it in case of an accident: step by step
The algorithm for conducting an independent trace examination in case of an accident is as follows:
- choosing a competent company;
- conclusion of a contract and payment for services;
- collecting a package of necessary documentation, including:
- situation diagrams;
- protocol;
- photographic materials from the scene of the accident;
- title documents;
- certificates from the police confirming the accident;
- written explanations of participants and witnesses of the accident.
- inviting an expert to inspect the accident site;
- agreeing on the place and time of vehicle inspection;
- waiting for the results of modeling situations from the scene of an accident;
- receiving a report on the work done.
How to challenge the results of a trace examination - 4 useful tips
Such a procedure is possible, although not so simple. They take her through the court.
Tip 1. Objectively evaluate the expert’s activities
See whether the objectives set during the examination were achieved. Make sure that the specialist does not exceed his authority.
When reading the expert opinion, be sure to follow the logical chains. They should not contain contradictions or wording that can be interpreted in two ways.
If you find even the slightest errors, insist that the results of the forensic trace examination be invalidated.
Tip 2. Carefully study the progress report
The conclusion drawn up by the expert should not contain deviations from the actual data. Because even small inaccuracies can change the course of the trial.
A properly compiled examination report contains:
- description of the circumstances under which the accident occurred;
- witness statements;
- information about the participants in the accident;
- presentation of information contained in traffic police documents;
- information from the accident scene inspection report.
The absence of any of the listed points is a legal reason to challenge the examination.
Tip 3. Insist on inviting an expert to the courtroom
This makes it easier to prove that the examination carried out is biased, as it was carried out with violations. This would be a good basis for requesting that the study be conducted again.
Directly in court, you can present to the expert all violations committed during the examination. If he does not provide an explanation, you will prove his incompetence and receive permission to re-examine.
Tip 4. Use the services of qualified lawyers
If you are sure that the expert’s mistakes are obvious, and you can prove it, you can appear in court yourself. But in order to be guaranteed to win the process, it is better to invite a professional lawyer as a representative.
A specialist can easily find shortcomings in the expert’s work and help you successfully challenge the results of the examination. Then you can find a more competent traceologist and get an objective study.
Pravoved, a legal assistance portal whose scope of activity extends throughout the country, will help you find a high-level lawyer.
We suggest reading a separate publication about the cases in which “Forensic Expertise” is prescribed.
On the topic of difficulties that traceological examination will help to avoid, watch the video.
Petition for trace examination of an accident
A petition to appoint a trace examination in case of an accident is a document that indicates the request of a citizen or organization to have an examination of evidence, traces, and the scene of the incident carried out in the case with the involvement of an expert. The petition is submitted in writing. Any participant in the paperwork can petition for a trace examination.
You can apply at any stage of the proceedings:
- Before the start of litigation at the preliminary investigation stage.
- In the court of first instance.
- At the appeal stage.
If the petition was filed at the appeal stage, the participant filing it must indicate a valid reason why he did not do so at previous court hearings and proceedings.
Of course, the best time to conduct a trace analysis is immediately after the incident. At this moment, the expert will be able not only to see all the traces left, but also the picture of the accident itself.
You can file and submit a motion at any time, but before the judge makes a final decision on the issue under consideration. The petition is written in free form. However, it is necessary to indicate the following mandatory information:
- details of the court, case number, full information about the participants in the case, date and signature of the applicant;
- the reasons for which the need for an examination arises and for which the petition is filed;
- to whom do you wish to entrust the examination;
- an approximate list of questions that the expert needs to answer;
- list of materials, documents, information that you can provide to the expert on your part
- indicate the type of transport and traceability examination.
Where to order a trace examination - review of the TOP-3 expert companies
In this section we will pay attention to several large companies that perform traceological examination. Do not forget that the cost of each study will be calculated individually.
1)
The organization has been operating since 2001 and has already accumulated extensive experience in conducting traceological and other types of examinations that are necessary in the event of damage to a car.
The company is a member of the Russian Federal Center for Forensic Expertise, and its experts are members of appraiser associations. Licensed software is used for examination. All services are provided very quickly.
Contact specialists directly on the website:
- ask questions to a car expert;
- get professional legal assistance;
- Send the most important and extraordinary questions directly to the director.
2) Center for independent examinations, assessment and technical research "Paritet-Consulting"
Here they take on even the most complex and non-standard tasks. All company experts have specialized education and diplomas confirming their qualifications. All of them are included in the register of expert technicians of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation.
In addition to the results of examinations and assessments, you can, if necessary, receive legal support, assistance and advice. As well as a review of the forensic examination, if its quality and reliability are in doubt.
The price for each type of service is indicated in the price list on the website. In addition, the company offers a free preliminary assessment of the situation, which will allow you to determine the feasibility of conducting a trace examination. To do this, materials and questions simply need to be sent by email.
3) Expert legal bureau “Honest”
The institution specializes in conducting forensic and pre-trial examinations of vehicles in Moscow, St. Petersburg and their regions.
More than 10 years of experience and a team of 20 experts of the highest category allow us to have no doubt about the quality of the research carried out here. More than 300 results are submitted to various courts every month.
If you need a trace examination, you can ask the expert questions directly in the office, by phone, or by email.
If the case is lost, you will be reimbursed up to 80% of the funds spent. Although in the company's practice only 1 such case was recorded.
Issues resolved by traceological examination
Traceology is a science whose subject of study is traces. An examination is prescribed in various cases when it is necessary to understand whether the traces left at the crime scene point to the criminal or, on the contrary, speak about the combination of circumstances that led to the incident.
The study is divided according to the number of participants in the event:
- sole;
- complex;
- commission.
It is possible to assign a repeated and additional procedure in order to classify objects, compare them, or determine the situation that led to the crime.
Traceology objects:
- evidence of a material nature;
- the material situation of the scene of the incident;
- procedural documents (protocols for examining the crime scene, examining the victim);
- reference materials, samples for identification (fingerprint database).
The list of questions that traceology reveals is extensive. The classification of subtypes of research will help you understand in more detail.
Human traces
Homeoscopic research studies traces left directly by humans:
- hands;
- feet (bare, in shoes or hosiery);
- teeth;
- epithelium of the head.
Thanks to this type of examination, the following tasks are solved:
- the presence of handprints on objects, their identification;
- clarification of possible features of the structure of the hands;
- how long ago the traces were left;
- number of participants in the crime.
Experts can easily determine which hand and even which finger left the imprint on the object being studied; gender is also calculated from such traces.
Questions that studying footprints can help answer are:
- foot size, structural features;
- style of shoes, stockings, socks;
- gender, approximate age and height;
- gait features, the presence of a prosthesis, orthopedic devices;
- method of movement (calm or fussy walking, or running of varying intensity);
- direction of movement of the participant in the incident.
Footprints make it possible to determine in some cases the mechanism of their occurrence, thereby helping to find out how a criminal, or a person not related to criminal actions, ended up in the place under study.
Teeth prints can be left by both the criminal and the victim, the examination finds out:
- what kind of tooth or teeth left the mark;
- presence of dentures, absence of teeth;
- structural features of the jaw;
- mechanism of fingerprint formation.
Lip prints on clothing, dishes or human skin sometimes help to identify the object that left them. However, first of all, it is necessary to determine whether they are suitable for identification.
The skin of the head (forehead, nose, cheek, cheekbone) tells about gender, sometimes about age, structural features and defects.
Microtraceology is distinguished separately; its subject is microparticles and miniature traces.
Mechanical examination
Such traces are classified as instruments of crime, actions performed by a person.
The examination of the alleged crime weapon determines:
- characteristics of the weapon (size, presence of notches);
- the presence of its traces on other objects;
- the direction and strength of the weapon used;
- relative position of objects at the time of use;
- sequence of blows, breaks, cuts.
Traces of dragging or wrestling are determined not only by the condition of the victim, but also by the presence of mechanical damage to clothing, marks on the grass, ground, or floor.
Cases of object binding do not go unnoticed by the expert. Based on the type of knot knitting and loop creation, a specialist will determine:
- binding mechanism;
- the presence of professional skills in tying (sea knot, “grapevine”, “bayonet”, “rabbit ears”, used mainly in mountaineering);
- left-handed or right-handed person tying the object.
The study of locks, first of all, reveals traces of burglary, the object of unlocking (master key, duplicate key), and determines the external or internal side of the mechanical impact. They are also looking into whether seals have been broken on various locks.
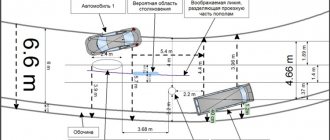
Transport expertise
Examination of vehicles and traces left by them in violation of traffic rules is a fairly extensive subgroup of mechanoscopic research.
Often, when writing the name of this examination, a double “s” is used. The error arose precisely because of motorists who associated the name of the study “traceological” with the highway.
The activities assigned to study the mechanism of the incident answer the following questions:
- which vehicle is guilty of traffic violations;
- identification of dents and scratches related to this incident;
- compliance of the at-fault vehicle with technical inspection standards;
- the legality of the driver’s actions to prevent a collision or accident;
- study of the structural features of tires, engine parts, transmissions and other important elements;
- driving mode of traffic rules participants (braking, skidding, excessive speed);
- suspected tire brand, model and other features of the vehicle that left the crime scene.
Thanks to modern developments, trace analysis makes it possible to reconstruct actions during an incident, to simulate any crime, according to the height, gender of the criminal or the dimensions and speed of vehicles.
They also distinguish taurological traceology, which specializes in traces of animals, and odorology, which identifies gaseous traces - odors.
Traces are detected using several methods:
- luminescent;
- thermal vacuum spraying;
- application of “Tsiacrin EO” glue.
The latter detects the presence of even old traces.
Who commissions the study?
Despite the fact that trace research is classified as a procedural process, that is, necessary during legal proceedings, an independent examination is also possible.
In the event that a participant in a road accident does not agree with the accusation or opposes the actions of a certain person and does not believe in justice, he can order an independent examination. Since civil disputes often take place without the participation of a court, extrajudicial investigation of traces is in demand.
Who performs the procedure?
A limited number of people are allowed to investigate a crime scene. A forensic expert who collects traces left by participants in an incident is called a traceologist (a forensic traceologist). That is, higher education must be in the specialty “forensic examination”.
Ballistas, materials scientists, forensic scientists, chemists, and biologists are brought in to help him, especially during a complex study.
How is the procedure performed?
The customer contacts private organizations specializing in conducting examinations to submit an application. There is also the option of contacting investigative authorities. Employees of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate apply directly to the forensic centers of the Central Internal Affairs Directorate and the Federation of Forensic Experts.
Next, the private individual writes an application for the provision of the service, and the police officers draw up a petition.
The organization conducts research according to the approved plan:
- preliminary inspection;
- detailed examination of the provided traces;
- evaluation stage of the results obtained;
- preliminary conclusions, their confirmation;
- drawing up a report, recording the results in the prescribed form, using a photo report.
The timing of the expert’s report depends on the scale of the problem. In particular, it will take more time to determine traces of an accident involving several cars, as well as in the case of a murder or attack on several objects.
According to the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the period for consideration of a case is usually set at no more than 2 months, which also includes the time frame for conducting the study. But, if more time is required for the examination, this period is increased.
According to the order of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation “On approval of methodological recommendations...”, the forensic expert is given a period of within 30 days to draw up a report, however, even here it is possible to increase the time criteria.
What documents are required?
The list of documents that the expert service staff will need depends on the identified problem.
If trace studies of a crime scene identified as a murder are required, a full report from the investigator, interrogator, and examination protocol will be required. Also, if the expert did not immediately go to the scene of the incident, photographs, shoe casts and other research objects will be needed.
To order an examination of traffic rules by a private person, you will need the following:
- certificate of an accident;
- case materials compiled by traffic police officers (photo tables, diagrams, protocol);
- technical passport of the car, information about the technical inspection completed.
The expert is provided with mandatory access to the vehicle, clothing and other materials from the persons involved in the accident.