Non-mechanical vehicles
These primarily include bicycles. They are vehicles, with the exception of wheelchairs, that have at least 2 wheels and are driven by the muscular energy of citizens and control them. Pedals or handles can be used for this. Motors can be installed on bicycles. Their maximum rated power does not exceed 0.25 kW. At the same time, they automatically turn off at speeds above 25 km/h. All of these parameters allow us to classify bicycles as non-mechanical vehicles.
VUZRU
Vehicle is a device designed to transport people, goods or equipment installed on it on roads.
In principle, everything is clear and simple. The criterion of a vehicle is its transportation function.
However, transport varies. And there are a huge number of reasons for its classification.
Vehicles can be divided into[1]:
- rail (tram) and trackless (the vast majority of vehicles that can move variably along the roadway, moving freely along the lanes);
- wheeled and tracked.
- cars, motorcycles, tractors and self-propelled vehicles, etc.
There can be many classification criteria.
According to the traffic rules, even a bicycle and a trailer are considered vehicles. These concepts are specifically defined in the Rules.
Definition from traffic rules (clause 1.2):
“Bicycle” is a vehicle, other than a wheelchair, which has at least two wheels and is generally propelled by the muscular energy of the occupants of the vehicle, in particular by means of pedals or handles, and may also have an electric motor of rated maximum power in continuous load mode not exceeding 0.25 kW, automatically switches off at speeds over 25 km/h.
The main distinguishing feature of the bicycle is the absence of any engine or an extremely low-power electric motor. However, the cyclist is the driver and is responsible for both traffic safety and violation of the Rules.
Since a cyclist is a full-fledged participant in road traffic, it should be remembered that the movement of cyclists on the roads - within the roadway or on the side of the road - is only permitted from the age of 14.
In reality, we can observe the most flagrant violations of traffic rules when teenagers who have not reached that age drive onto the roadway. (see Attachment)
Definition from traffic rules (clause 1.2):
“Trailer” is a vehicle that is not equipped with an engine and is intended to be driven in conjunction with a power-driven vehicle. The term also applies to semi-trailers and trailers. (see Attachment)
A trailer is a special vehicle. But driving with it may require opening a new category of driver’s license (with the letter “E” attached - BE, CE, DE, etc.). This is necessary if the trailer has a permissible maximum weight exceeding 750 kg.
However, there are options when the permitted maximum weight may not exceed 750 kg. (see Attachment)
In this case, opening a new category of rights (BE, CE, DE, etc.) is not required.
Next, I would like to focus on motor transport, as the most representative segment in the vehicle environment. Both the most famous and widespread is the classification that determines the purpose of vehicles [2]:
1) passenger cars (for individual transportation of passengers);
2) passenger, intended for mass transportation of passengers (for example, a bus);
3) cargo (for transporting goods, less often people);
4) special (operational services, tow trucks, technical assistance and other vehicles performing specialized functions).
However, despite the incredible abundance of vehicle classifications, the concept of “motor vehicle” is of paramount importance for traffic regulations.
Mechanical vehicle.
Traffic rules regulate the movement of mainly mechanical vehicles. The “lion's share” of the Rules is devoted precisely to this aspect of road traffic.
To drive a mechanical vehicle, a person must have a driver's license of the appropriate category. In the vast majority of cases, a motor vehicle requires special state registration and registration plates (or “numbers”).
Definition from traffic rules (clause 1.2):
“Motor driven vehicle” is a vehicle driven by an engine. The term also applies to any tractors and self-propelled machines.
The most important indicator of a mechanical vehicle is the presence of an engine. (gasoline, gas, diesel, electric, water (or steam)). In the future - nuclear.
In other words, a mechanical vehicle is capable of moving along roads independently (due to the presence of a power unit). And the driver of a mechanical vehicle, in order to drive it, must undergo special training, pass a qualification exam and obtain a driver’s license corresponding to the category of the vehicle.
Traffic regulations do not define cargo and passenger vehicles, but they specifically distinguish two types of mechanical vehicles:
- motorbike;
- moped.
There has been a lot of confusion in the motor vehicle community lately. The situation is especially difficult for the average person, because vehicles claiming to be “motorcycle-like” have sharply increased in number.
Even the very concept of “motorcycle” in traffic regulations contains some uncertainty.
Definition from traffic rules (clause 1.2):
“Motorcycle” is a two-wheeled motor vehicle with or without a side trailer. Three- and four-wheeled mechanical vehicles with a curb weight of no more than 400 kg are considered motorcycles.
The names of the following vehicles are consonant with the motorcycle:
1) ATV;
2) quadricycle;
3) tricycle.
However, these are fundamentally different vehicles that are not motorcycles. They have different structural and functional characteristics.
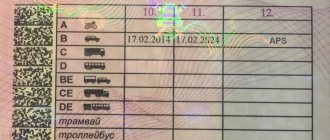
The easiest way to determine whether a vehicle is a motorcycle is by looking at the documentation for it: in the PTS (vehicle passport) or technical passport (registration certificate). (see Attachment)
There is a special mark reflecting the category and type of vehicle to which this vehicle belongs. Category A will mean belonging to motorcycles.
But a moped (or scooter, mokiki and similar vehicles) is a special category.
Relatively recently - in the previous edition of the traffic rules - a moped (or scooter) was not a mechanical vehicle. To drive it, you did not need to study and obtain a driver's license (“license”).
Now the situation is fundamentally different.
Definition from traffic rules (clause 1.2):
“Moped” is a two- or three-wheeled mechanical vehicle, the maximum design speed of which does not exceed 50 km/h, having an internal combustion engine with a displacement not exceeding 50 cubic meters. cm, or an electric motor with a rated maximum power in continuous load mode of more than 0.25 kW and less than 4 kW.
Now a moped is a mechanical vehicle, and driving it indicates the need to obtain a driver’s license of a new category - category M.
And for this you should undergo specialized training at a driving school. True, every holder of a driver’s license of any category can drive a moped or scooter.
The main subject (“participant”) of road traffic is a mechanical vehicle. It was for him that traffic rules were actually created.
Route vehicle[3].
A special type of vehicle is a route vehicle. It has a special status on the road. Drivers of such vehicles are allowed some “liberties”, which are deviations from general traffic rules. Thus, they are allowed to ignore some prohibitory and mandatory signs, signs of special instructions, etc. A lane for traffic is allocated especially for them on the roadway, and places for boarding and disembarking passengers are indicated by a special sign and/or markings.
Definition from traffic rules (clause 1.2):
“Route vehicle” is a public vehicle (bus, trolleybus, tram) intended for transporting people on roads and moving along a set route with designated stopping places.
Let us designate such vehicles. Judging by the definition of the traffic rules themselves, these are bus, trolleybus and tram. To these should also be added route gazelles (with which, by the way, an irreconcilable struggle is being waged today as an unsafe route vehicle).
But every bus or minibus is actually a route vehicle. Of course not! The rules clearly introduce special functional criteria for them:
- transportation of people (passengers) on roads;
- a strictly established route (with a specific route number);
- designated stopping places intended for boarding and disembarking passengers.
And it turns out that the driver moving along the route in such a vehicle will be classified as a driver of a route vehicle with all the ensuing “benefits” for him (we will talk about them in special sections of the traffic rules).
But if the driver, after a working day, having dropped off passengers at the “terminal”, moves home, to the garage, to the parking lot of his minibus, then his vehicle is no longer considered a route vehicle. Accordingly, all “benefits” disappear. And even in the morning - until the moment you set out on the route - the gazelle is not considered a route vehicle.
Thus, at present there is no unified classification of vehicles, incl. road (auto-moto) vehicles. At the same time, while attempts are being made in the scientific literature to distinguish vehicles according to the criterion of classifying them as sources of increased danger, in judicial practice there has been a strong position that, in essence, all vehicles with an engine are classified as such.
Ownership of a car is in no way related to whether a person has the right to drive a car (the so-called driving license). A citizen (individual) may not have driving skills or a driver’s license, but has the right to own, pledge or have any other right any number of cars of any value and in any condition. Moreover, a citizen may be in a state where, in principle, he cannot be granted the right to drive (minority, incapacity), but this will not be an obstacle to being the owner of a car. And vice versa - having a driver’s license in no way obliges a citizen to purchase a car; he may well use his license to drive someone else’s car. In general, no violations of traffic rules by the driver, incl. and those that can serve as a basis for deprivation of the right to drive (violation of traffic rules) cannot serve as grounds for changing, limiting, and, even more so, terminating subjective rights to a car[4].
It is possible (if there are appropriate grounds) to deprive a citizen of the right to drive (subjective administrative law) by confiscating his driver’s license. But in no case can a person with a driver’s license of the established category be prohibited from driving a specific car, be prohibited from alienating this car or otherwise disposing of it, seizing it against the will of the owner, creating actual obstacles to its use, or subjecting the car to so-called detention or seizure. Both the seizure of the car and the restriction of the owner in the use and (or) disposal of the car will be illegal in these cases. Article 301 of the Civil Code allows the owner to reclaim his property from someone else’s illegal possession (i.e., vindicate), and Art. 304 of the Civil Code - to demand the elimination of violations of other powers, even if not related to deprivation of possession.
Thus, having considered the questions of the first chapter and based on the above, we can give the following definition of a vehicle as an object of civil law: a vehicle is a device driven by an engine, intended for the transportation of passengers, luggage, cargo or equipment installed on it by road, rules of use which are regulated by civil legislation, transport legislation and charters, as well as traffic rules and technical operation rules.
When considering a vehicle as a source of increased danger, it is necessary to establish signs of a source of increased danger. Over the entire period of research into this concept, scientists have developed a limited list of such features:
- the presence of potentially harmful properties;
- incomplete control of it by a person, the severity of the consequences of its leaving the control of a person;
- high probability of causing harm to others;
- the complexity of managing sources of increased danger, which requires special training of workers and strict regulation of the activity process itself by establishing safety rules;
- the need for increased caution and vigilance during its operation;
- the possibility of accidental, spontaneous harm during its operation, even when measures are taken to prevent it.
[1] Civil law. T.1. Abramova E.N., Averchenko N.N., Baigusheva Yu.V., Ed. Sergeeva A.P. - M.: 2014. - 880 p.
[2] Civil law. General and Special parts: Textbook / Poponov Yu.G., Fokov A.P., Cherkashin V.A., Cherkashina I.L., M.: KnoRus, 2015 – 688p.
[3] Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Immovable and movable things. Securities. Protection of honor, dignity and business reputation. Protection of private life: article-by-article commentary to chapters 6 - 8 / V. V. Andropov, B. M. Gongalo, P. V. Krasheninnikov, etc.; edited by P. V. Krasheninnikova. -M. : Statute, 2014. -208 s.
[4] Belov V.A. A car as an object of citizen’s property rights // Legislation.
1998. № 11, 12.
Special category
Mopeds are mechanical means (transport). This is due to the presence of an internal combustion engine or an electric motor. Meanwhile, mopeds are included in the category of non-motorized vehicles. This is explained by the fact that their maximum design speed does not exceed 50 km/h, and the working volume of the motor is 50 m3 (or the rated power with a continuous load of more than 0.25 and less than 4 kW). Other vehicles are defined in a similar way. These are primarily scooters, motorcycles and other similar vehicles with engines.
Frequent violations of operating rules
Drivers, unfortunately, do not always comply with traffic regulations and, because of this, provoke the creation of emergency situations on the road. Among the most common violations of the rules for operating mechanical vehicles are the following:
| Did not find an answer to your question? Call a lawyer! Moscow: +7 (499) 110-89-42 St. Petersburg: +7 (812) 385-56-34 Russia: +7 (499) 755-96-84 |
- Exceeding the speed limit. Each section of the route has its own speed limits. In the city, driving speeds of up to 60 km/h are allowed, and in courtyard areas generally up to 20 km/h. Outside the city, the figures can increase to 70-90 km/h, but on highways, on the contrary, you cannot drive slower than the established speed limit.
- Failure to maintain distance between cars. The traffic rules do not establish strict requirements for the distance between cars. And if an accident does not happen, then no one will be fined for a short distance. However, it is failure to maintain a distance that leads to the majority of accidents, when the driver simply does not have time to react and take the correct actions.
- Communicating on the phone while driving without the use of special electronic means that allow you not to be distracted from the road while talking.
- Turn signals not turning on. The inability of the vehicle behind to recognize the planned maneuver leads to the creation of emergency situations.
Do not also forget about the requirement to use near daylight at any time of day (even during daylight). Drivers often forget about this and receive fines for non-compliance with the norm.
Important point
Driving a vehicle classified as non-motorized does not require a driver's license. The vehicles themselves do not undergo registration; signs (numbers) are not provided for them. Meanwhile, we should not forget that the persons who own them are drivers. In this regard, driving a non-mechanical vehicle must be carried out in accordance with traffic rules.
Compliance between the category of driver's license and the category of technical regulations
Compliance between the category of driver's license and the category of technical regulations
| Driving license category | Category of technical regulations |
| A, A1 | L3-L5 |
| B (passenger cars) | M1 |
| B (freight) | N1 |
| B1 | L6-L7 |
| C | N2-N3 |
| D | M2-M3 |
| E | O2-O4 |
| M | L1-L2 |
*trailers of category O1 can be driven without category E on the driver's license.
Infographics from the Moscow traffic police
Other articles in this section:
- Toll roads and traffic rules in Russia
- Russian traffic rules
- Table of fines for traffic violations in Russia
- Automobile codes of regions of Russia
Maximum permissible weight
It characterizes the weight of the vehicle with cargo, passengers and driver. The permitted weight is set by the manufacturer and is considered the maximum permissible. Let's understand the terminology. The maximum permissible weight of a vehicle with passengers, cargo and driver is considered to be the maximum. Exceeding the established indicator is prohibited. This is due to the fact that under high loads (greater than those provided by the manufacturer), the car body, brake system, engine, suspension, steering part will not be able to function normally. Accordingly, there is a risk of creating an emergency situation. The maximum permitted weight is to a certain extent a theoretical indicator, which is prescribed in the vehicle title and registration certificate. Often many people confuse it with the actual weight of the vehicle. The key difference between these parameters is that the permitted mass is set once and for all. However, the actual weight may constantly change. However, in any case, its value should not exceed the permitted mass.
Weight as a criterion of differentiation
Vehicles are classified according to their permitted weight. Trucks are divided into 2 categories according to this indicator. The first includes vehicles with a permissible weight of no more than 3.5 tons, the second - more than 3.5 tons. This figure acts as a kind of indicator of the size of cars. In this regard, trucks whose permissible weight is less than 3.5 tons are included in a category that also includes passenger cars.
Correspondence table with categories on rights
Using this table you can compare the classification used in the technical regulations with the driving categories used in the traffic rules.
| Category tech. regulations | Category of rights |
| L3-L5 | A, A1 |
| M1, M2, N1 | B |
| L6-L7 | B1 |
| N2-N3 | C |
| M2-M3 | D |
| O2-O4 | E |
| L1-L2 | M |
This is interesting: Ammonia (hydrogen nitride)
Permitted weight of coupled vehicles
The totality of their weight parameters is taken as the maximum permissible weight of vehicles moving as a whole. To understand this situation, it is advisable to refer to the concepts of “trailer” and “road train”. The first is a vehicle that is not equipped with a motor and is used to move in conjunction with a mechanical vehicle. A road train refers to devices that are coupled to a trailer. Accordingly, if there are several vehicles in the composition, including those without engines, the total permissible weight will correspond to the sum of their permissible weight provided by the manufacturers.
Description of rail and trackless vehicles
“Mechanics” is what people often call a car with a manual transmission.
In order to move quickly and comfortably, rail vehicle installations require specially equipped roads. They are characterized by the presence of special guides, which ensures the formation of an entire motor transport system using them. By type, rail vehicles can be conventional, universal, narrow-line, monorail and combined.
Absolutely all cars are adapted to fully move along railway tracks. Rail vehicle installations are presented in the form of high-speed trains that have a magnetic levitation. Certain types of vehicles are characterized by the presence of an air cushion.
A tram is a street and partly rail-based vehicle that is characterized by general use. With its help, passengers are transported along predetermined routes. The operation of this vehicle is carried out using electric traction.
The trackless group of vehicles consists of buses, cars, trolleybuses, all-terrain vehicles, motorcycles, tractors, bicycles, all-terrain vehicles, trolleybuses and cotton pickers. Trackless vehicles are absolutely all land vehicles, the movement of which does not require the use of rail tracks. Full movement of equipment is ensured by a flat, hard surface.
Trackless vehicles are characterized by very good maneuverability, regardless of the type of road surface. A distinctive feature of rail and trackless vehicles is the need to use railway tracks for their movement.
Route vehicle
It is a technical vehicle intended for public use. This category includes buses, trams, and trolleybuses. Their main function is to transport people along a set route with stops at designated places. Such vehicles are determined by the following criteria:
- Belonging to the passenger transportation infrastructure.
- Movement along the approved route.
- Making stops at designated areas and upon request.
Water transport
This is one of the classic types of vehicles. Such transport is intended for transportation along artificial (reservoirs, canals) and natural (lakes, rivers, seas, etc.) waterways.
Unlike air, water transport is one of the cheapest after pipeline transport. That is why almost everything is transported by such vehicles: from building materials to minerals. And such watercraft, such as ferries, are even capable of transporting other vehicles.
But passenger traffic has recently become significantly less. This is justified by the rather low speed at which ships move from one seaport to another.
The main types of vehicles moving along waterways: surface (boats, boats, liners, ships) and underwater vessels.
Specifics
It should be noted that one of the key criteria for route vehicles is the availability of a working schedule. Why is this feature particularly highlighted in the definition? The fact is that while the vehicle is not on the route, it will not be considered public transport. For example, a passenger GAZELLE driving to a garage or parking place after a shift is an ordinary vehicle. There are certain concessions and privileges for public transport. For example, the driver of a route vehicle may ignore a number of prohibitory or injunctive signs. Special lanes are provided for this type of transport. They are distinguished by special markings and signs.
Vehicle purchase and sale agreement
Many vehicle owners need to sell their car. At the same time, a contract for the sale of the vehicle is drawn up. Here are some recommendations for how to compile it correctly. The document can be filled out by hand or on a computer. Particular attention should be paid to key terms. The contract must contain a number. For example, 01/2016. Subsequently, this number will be indicated in the PTS. The document contains the place and date of the transaction. The passport details of the seller and the buyer must be indicated. Information about the car must also be present in the document. They are copied from the certificate and PTS. The price of the car is set by the parties to the transaction themselves. The amount is written in numbers and words. Immediately before signing, the owner hands over the keys and documents, and the buyer hands over the money. In addition to the contract, a vehicle acceptance certificate is also drawn up.
Additionally
After signing the contract, the new owner is indicated in the PTS. Within ten days from the date of the transaction, the buyer must register the car. At the end of the established period, the former owner can check the fact of registration of the vehicle. In this situation, a signed agreement will be useful to the former owner. The citizen does not have a vehicle, but it is registered with him - what to do in this case? The former owner has the right to terminate registration by submitting a corresponding agreement to the traffic police. If the policy has not expired on the date of the transaction, the citizen has the right to return the money under it. It should be taken into account that the calculation of unused days begins on the calendar date following the day of termination of the insurance agreement.
Vehicle rental
It is regulated by the provisions of the Civil Code. The Code provides for two types of charter: with and without crew. Their definitions are given in Art. 632 and 642. The subject of the agreement is exclusively vehicles intended for the transportation of baggage, passengers and cargo. Renting a vehicle with crew involves two obligations. One is directly related to the provision of a vehicle for use. The second concerns the provision of services by the crew. The differences in regulatory regulation of these types of transactions are as follows. Responsibilities for operating a vehicle provided without a crew are assigned to the lessor. In the second case, they are performed by the tenant. The payment made by the user is called freight. The crew of a leased vehicle is subordinate to both the lessee and the lessor. Liability for damage to third parties is distributed depending on a number of circumstances. So, if the vehicle is provided without a crew, it is borne by the lessee. He may be released from liability if he proves that the harm was a consequence of the actions of the victim or force majeure. When renting a car with a crew, the lessor is responsible for damage.
Transporting machines
While the types of vehicles described are fairly well known to everyone, there are several other types of devices that also fall into this category, but are less noticeable. These types of machines are equipment that is used for continuous delivery of cargo in a horizontal, vertical or inclined direction. Most often, delivery of a variety of bulk materials is provided. As for the principle of operation of these machines, especially those used in the construction industry, it is worth highlighting conveyors, as well as pneumatic conveying installations.
With the help of conveyors, it is possible to ensure delivery in a horizontal or slightly inclined position to the desired point without any problems. Most often, delivery is carried out over long distances, and the cargo is bulk and piece material. As for the principle of operation, only conveyors can be distinguished from continuous machines. However, intermittent devices can also be used. These include electric or carburetor type trolleys. Carts without an engine can be used.